Genetic Eye Disease Related Terms and Resources
All content on Eyewiki is protected by copyright law and the Terms of Service. This content may not be reproduced, copied, or put into any artificial intelligence program, including large language and generative AI models, without permission from the Academy.
Introduction
The ophthalmologist’s role in the management and diagnosis of genetic disorders can be critical for patients, families and referring providers in the steadily advancing field of genetics. Genetic testing can be a useful medical tool in ophthalmology to help confirm or rule out a suspected inherited ocular disorder, provide important information of inheritance patterns and risk of recurrences for families, and help guide clinical management, appropriate referral and surveillance decisions. Furthermore, genetic testing may also provide a societal benefit in improving the understanding of genes, genetic diseases, and future treatments.
Testing offered may be clinical or research-based, and may be carried out in the prenatal period, as part of the newborn screening, used to determine carrier status, or can be used for diagnostic purposes. Common genetic tests used to confirm or make a diagnosis include, but are not limited to, chromosomal karyotype or microarray, fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) and sequencing. (See Section 2 and Section3/Table 1)[1] [2] [3] [4] Advances in our knowledge of both genetic disease and diagnostic technological capabilities continues to exponentially improve, however, there are still many limitations in each of the available genetic diagnostic testing modalities. In addition, the ethical concerns and psychosocial impact of the genetic test results can be substantial for the patient being tested, the family members, and for the clinician and medical team involved.[5] Financial burdens also exist, as costs can range from hundreds to thousands of dollars for a single test. Many insurance carriers now have guidelines in place to determine medical necessity that generally include examining the clinical validity of the genetic test being requested, the clinical signs and symptoms present, the risk involved for the disease of concern based on family history, and how the result from the test will ultimately affect the medical management.[6]
Tests results may return as positive indicating a change in the area of interest, negative indicating there was no change found, or as a variant of uncertain significance (VUS) indicating a change has been found but that the significance of this change is not well understood. Therefore both the decision to undergo testing and the interpretation of the results are complex entities and should involve trained individuals with an expertise in this area and knowledge of genetic counseling. Genetic testing is generally performed by a geneticist or a genetic counselor, or ordered in consultation with them.
Recommendations for genetic testing include 1) to test for a disorder for which the causative genes have been identified, 2) use a Clinical Laboratories Improvement Amendments (CLIA) approved laboratory, 3) order the most specific test and avoid unnecessary parallel testing, 4) avoid testing for genetically complex disorders for which no treatment or surveillance guidelines exist, and 5) avoid genetic testing in asymptomatic minors when involving untreatable disorders except in rare circumstances.[7] Several genetic terms and resources are listed as follows to assist in managing the numerous and steadily growing list of ocular inherited diseases. (See Section 2 and 4)[1][2][3][4][8]
Additionally, the phenotypes of many ophthalmic genetic conditions have been well characterized, and the ophthalmic exam may offer important information in detecting the underlying genetic disorder. Presented in the following sections are reported eye features, inheritance patterns, known associated gene or chromosomal abnormality, and MIM reference number for selected genetic diseases.[9] [10] [11][1] [12] [13] [14] [15] [16] [17] [18].
Definitions of Common Genetic Terms
| TERM | DEFINITION |
|---|---|
| Adeno-associated virus (AAV) vectors | Vectors derived from adeno-associated viruses, and the most frequently used delivery systems in ocular gene therapy. |
| Alleles | A variant of a gene located at a certain locus. |
| Amino acid sequence | Refers to the order of amino acids in a polypeptide chain. |
| Amino acids | A class of biological molecules characterized by an amine and carboxylic group along with a particular functional group. They are the main building blocks of proteins and have other important biological functions. |
| Aneuploidy | The state in which one or more extra or missing chromosomes is detected. |
| Anomaly | An anatomical departure from the phenotype present in the reference population. |
| Association | Unrelated pattern of anomalies in occurrence more often than expected by chance. |
| Autosome | A chromosome that is numbered and not considered a sex chromosome. |
| Autosomal dominant inheritance | An inheritance pattern in which only one copy of a particular autosomal chromosome is needed in order to produce the effects that the inherited chromosome presents with. |
| Autosomal recessive inheritance | An inheritance pattern in which two copies of a particular autosomal chromosome is needed in order to produce the effects of those particular inherited chromosomes. |
| Carrier testing | A form of genetic testing used on individuals that may not present with any genetic disorder but are at risk of passing down the a trait due to being a carrier. This usually relates to being a carrier of an abnormal autosomal recessive or X-linked disorder. |
| Central dogma of Molecular Biology | Describes the flow of genetic material in that DNA encodes for RNA (transcription), which in turn then encodes for proteins (translation). Exceptions to the classic dogma are now known to exist. |
| Chromosomal Karyotype | A photographic representation of an individual cell's chromosomes that is used to analyze the number and structure of the chromosomes. |
| Chromosomal Microarray | Evaluates the genome in a high resolution by utilizing arrayed small DNA pieces to provide a locus by locus measurement of DNA copy number variation at numerous loci simultaneously. |
| Chromosome | An organized and packed structure of DNA, RNA, and proteins located within a cell. |
| Chromosome Translocation | An abnormality that involves the exchange of genetic material of non-homologous chromosomes. Translocations can involve the exchange of equal amounts of material (balanced) or involved additional or missing material (unbalanced). |
| Clinical genetic testing | Genetic testing performed to discover information for the patient and family involved. |
| Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) | Laboratory testing U.S. federal regulatory standards that was first established in 1988 that requires certification for any lab prior to performing clinical diagnostic testing on human samples. The Center for Disease Control (CDC), Center for Medicaid Services (CMS), and the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) play a role in the function of CLIA. |
| Cloning | A process that consists of creating identical copies of DNA, a cell, or an organism. |
| Consanguinity | Used to describe genetic relatedness between individuals due to a common ancestor of origin. |
| Consultand | The person in the family that presents for a genetic counseling evaluation regarding a known or potential inherited condition. |
| De novo (sporadic) mutation | An altered gene that appears in the germline or fertilized egg that was not manifested in the family lineage, particular both of the parents. |
| Deletion | Change in the DNA sequence involving a portion of the DNA being removed. |
| Deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) | A biological molecule, double stranded, that encodes the genetic information of an organism. |
| Direct-to-consumer genetic testing | Genetic testing marketed and sold directly to consumers without the involvement of healthcare professionals. |
| Direct-to-consumer genetic testing through physician | Genetic testing marketed directly to consumers and physicians, and requires the physician to order the test. |
| Disease | Condition involving abnormal cognitive or physical function. |
| Duplication | Change in the DNA sequence involving an extra copy or copies of a portion of the DNA. |
| Exome | The part of the genome that corresponds to the complete set of exons. |
| Exons | Sequences in the DNA that corresponds to protein coding regions. |
| Fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) | Uses a targeted approach to analyze a specific sequence of a chromosome. The technique consists of using a specific probe DNA that is labeled and is hybridized to a sample DNA of interest. Recording of the labeled hybridization, or lack of, can then be analyzed. |
| Frameshift mutation | Change in the DNA sequence, either an insertion or deletion, not a multiple of three, which causes a shift in the reading frame. |
| Genes | A sequence of DNA that corresponds to a unit of hereditary information, usually coding for a protein. |
| Gene therapy | The experimental process of inserting genes for the purpose of treatment. |
| Genetic counselor | A health professional specialized in the area of genetics and counseling about various genetic information to individuals. |
| Genetic Information Nondiscrimination Act (GINA) | Legislation passed by the US Congress that prohibits employers and health insurance agencies from using genetic information in decisions. |
| Geneticist | An individual specialized in the study of genetics, which is composed of genes, heredity, and variation. |
| Genome browser | An online site that contain a collection of genomic data information. |
| Genome-wide association study (GWAS) | A technique that is used to study genetic markers across complete sets of DNA in different people in order to find genetic variation in a particular trait. |
| Genotype | The genetic makeup of an individual usually referring to a specific set of alleles or traits. |
| Germinal mutation | A change in the DNA sequence in the germline, and therefore can be passed on to the next generation. |
| Germline | The cell line in which the gametes are formed from. |
| Hemizygosity | State when only one copy of a gene is present in a diploid cell. |
| Human genome project | An international research study that sequenced the entire human genome and determined the genes that are encoded. |
| Incomplete penetrance | Refers to the presence of a gene change that is not phenotypically expressed in some individuals, but is expressed in others. |
| Insertion | Change in the DNA sequence involving an additional amount of DNA added in a new location. |
| Introns | Non-coding sequence found in DNA that is usually excised before translation. |
| Loss of heterozygosity (LOH) | Presence of only one copy of an allele such as due to a loss of a portion of a chromosome within a tumor tissue. |
| Malformation | A non-progressive congenital anomaly. |
| Massively parallel sequencing | High-throughput DNA sequencing that allows for numerous strands of DNA to be sequenced in a parallel fashion. Also called next-generation sequencing. |
| Meiosis | A form of cell division consisting of two nuclear division of a diploid resulting in the formation of haploid gametes. |
| Mendelian genetics | Genetics inheritance pattern proposed by Gregor Mendel that is composed of three main laws. The Law of Segregation states that allele segregation results in one allele per gamete. The Law of Independent Assortment states genes from different traits segregate independently. Law of Dominance states that alleles may be dominant or recessive and dominant alleles overshadow recessive alleles. |
| Missense mutation | Change in the DNA sequence involving a single base pair which causes an amino acid being substituted for another. |
| Mitochondrial inheritance | A form of inheritance from the genetic material located within the mitochondria. This form of inheritance is maternal and is always inherited due to being part of the ovum. |
| Mitosis | A form of cell division in which somatic cells produce identical daughter cells. |
| Mosaicism | The presence of two or more cell populations that differ in their chromosomal genotype. |
| Multifactorial inheritance | A combination of various genetic and environmental factors that contribute to the development of a trait. |
| Mutation | A change in the DNA sequence of a gene. |
| Newborn screening | Testing performed on newborn babies to detect for a wide variety of disorders. |
| Nonsense mutation | Change in the DNA sequence involving a single base pair that results in a premature stop codon, which leads to a shortened protein. |
| Nucleic acid sequence | Refers to the arrangement of letters that make up the nucleotide order in RNA and DNA. |
| Nucleotide | A nitrogenous base attached to a phosphate group and a pentose sugar molecule. A ribonucleotide, main unit of RNA, is composed of a phosphate group, a ribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base (Adenine(A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), or Uracil (U)). A deoxyribonucleotide, main unit in DNA, is composed of a phosphate group, deoxyribose sugar, and a nitrogenous base (Adenine (A), Cytosine (C), Guanine (G), or Thymine (T)). |
| Obligate carrier | Individual that must be a carrier of the genetic mutation of concern based on the known disorder inheritance pattern and family history obtained. |
| Ovum | A mature female haploid gamete. |
| Panel tests | Used in order to assess for mutations in multiple genes. |
| Pedigree | A genetic representation of a family lineage that demonstrates various inheritance patterns in the family tree. |
| Personalized medicine | A form of medical practice that uses an individual's genetic makeup to guide treatment. |
| Pharmacogenetics | A branch of pharmacology that studies the genetics responses to drug treatments. |
| Phenotype | The observable physical representation of an expressed gene. |
| Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) | Technique that allows a short sequence of DNA or RNA to be amplified. |
| Proband | An individual that is being studied on in genetics studies. Usually refers to the first affected family member with a genetic disorder or trait that begins the study of the family. |
| Proteins | A class of biological molecules that are composed of chains of amino acids. |
| Reflex testing | Automatic subsequent testing that takes place after an initial testing result. |
| Repeat expansion | Change in the DNA sequence involving consecutive repeated portions of short amounts of DNA. |
| Research genetic testing | Genetic testing performed as part of a research study to advance our knowledge of understanding genetic diseases, genes, and testing methods which may or may not provide immediate beneficial information to the patient or family involved. |
| Ribonucleic acid (RNA) | Biological macromolecule, single stranded, which primarily conveys information from DNA to control protein synthesis. |
| Sanger (dideoxy) sequencing | A technique for DNA sequence analysis that utilizes dideoxy nucleotides that will terminate the growing chain. |
| Sequencing | The process of determining the sequence of a part of the genome. |
| Silent mutation | Change in the DNA sequence that does not actually change the protein sequence. |
| Single gene tests | Analyzes a single gene in a sample DNA of interest in order to determine any abnormalities or absence of that single gene. |
| Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) | A form of DNA sequence variation in which a single nucleotide differs in a particular genome location in two or more members of a population. |
| Somatic | Any cell of the body excluding the gametes. |
| Somatic mutation | A change in the DNA that occurs after the conception period, therefore not passed on to the next generation. |
| Sperm | A male reproductive cell used in fertilization. |
| Splice site mutation | Change in the DNA sequence involves the location where intron splicing occurs. |
| Substitution | Change in the DNA sequence that replaces one base for another base. |
| Syndrome | Causally related pattern of anomalies. |
| Uniparental disomy | A genetic inheritance situation in which both members of a chromosomal pair or both segments of chromosome are inherited from one parent and neither is inherited from the other parent. |
| Variant of uncertain significance (VUS) | A variation in a gene sequence in which the association of the variation with any disease is unknown. |
| Whole Exome Sequencing | A technique used to analyze the entire coding sequence, exons, of a DNA sample of interest. The DNA sample is compared to a control sample by detecting any changes in nucleotide sequences. |
| Whole Genome Sequencing | A technique that determines the entire DNA sequence in a genome. |
| X-linked dominant inheritance | A form of inheritance in which a dominant gene is carried on an X chromosome and is expressed with only one copy necessary. |
| X-linked recessive inheritance | A form of inheritance in which a recessive gene is carried on an X chromosome. Only requires one copy to be expressed in a male and two copies to be expressed in a female. |
| Zygote | A diploid cell formed from the fusion of a sperm cell and an ovum. |
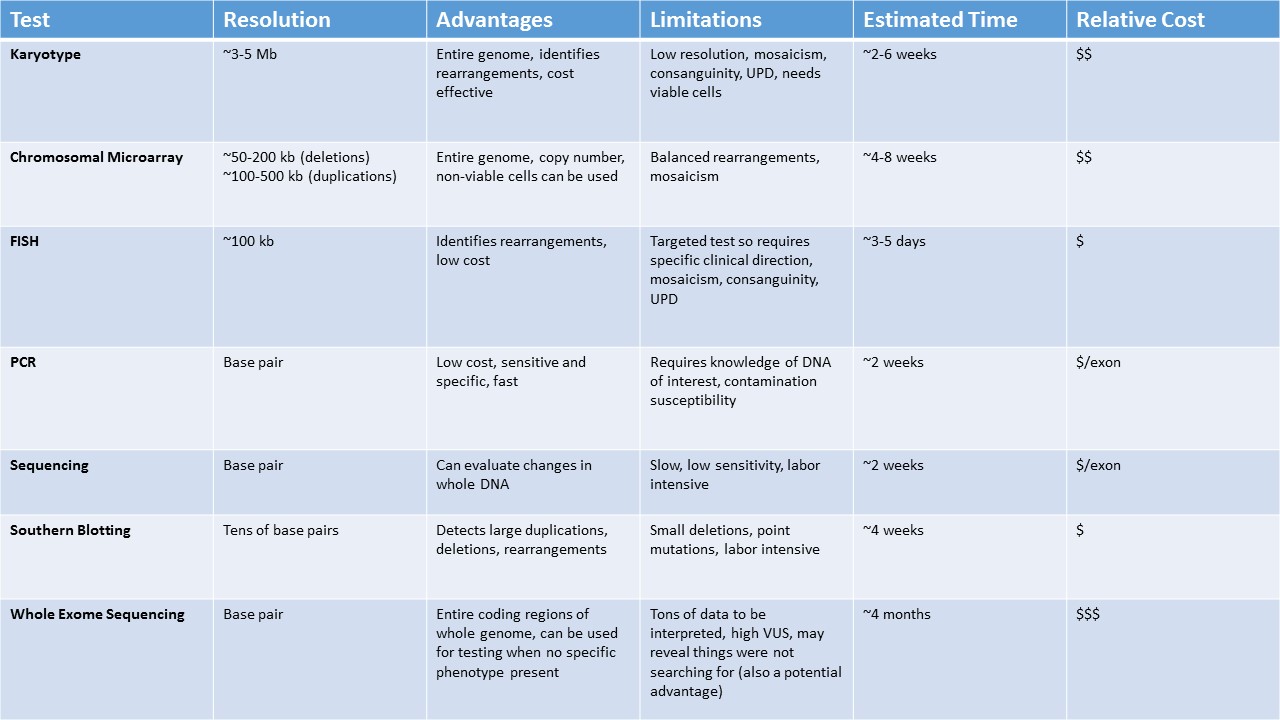
Table1. Comparison of Selected Genetic Tests
Genetic Resources
| SITE HEADING | DESCRIPTION | WEBSITE URL |
|---|---|---|
| American Academy of Ophthalmology (AAO) Recommendations for Genetic Testing of Inherited Eye Diseases | AAO task force's 2014 recommendations for ophthalmic genetic testing. | https://www.aao.org/clinical-statement/recommendations-genetic-testing-of-inherited-eye-d |
| American Board of Genetic Counseling | The organization in charge of giving credential certification in the field of genetic counseling in the United States and Canada. | https://www.abgc.net/ |
| American College of Medical Genetics | An organization composed of various individuals with specializations in genetics focused on the practice of medical genetics. | https://www.acmg.net/ |
| American Society of Human Genetics | Professional organization for specialist in human genetics. | http://www.ashg.org/ |
| Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology | Online encyclopedia and database atlas of genes, cytogenetics and cancer diseases that includes an overview of eye tumors | http://atlasgeneticsoncology.org//Tumors/EyeTumOverviewID5272.html |
| Children's Craniofacial Association | Educational resource and patient support for craniofacial syndromes | http://www.ccakids.com/ |
| ClinicalTrials.gov | A database that contains clinical studies of human participants from around the world. | http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/ |
| FACE2GENE by FDNA | A search and reference application that utilizes Facial Dysmorphology Novel Analysis (FDNA®) technology to detect dysmorphic features from facial photos | http://www.fdna.com/ |
| GeneCards | Comprehensive database containing information on known and predicted human genes. | http://www.genecards.org/ |
| GeneReviews | Publications consisting of standardized and clinical information for the diagnoses, management, and treatment of patients with inherited conditions. | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1116/advanced/ |
| Gene Tests | Information about clinical and research testing for genes. | https://www.genetests.org/ |
| Genetic Alliance | Nonprofit health advocacy group with a network of over 1,200 disease advocacy organizations that has a focus of promoting health in genetic research and technology. | http://www.geneticalliance.org/ |
| Genetic and Rare Disease Information Center (GARD) | A database that is part of the NIH that provides useful information about genetic and rare diseases. | http://rarediseases.info.nih.gov/gard |
| Genetics Home Reference | A website that provides information about genetic variations. | http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/ |
| Geneva Foundation for Medical Education and Research (GFMER) Atlas of Developmental and Genetic Diseases | Atlas of developmental and genetic eye diseases. | http://www.gfmer.ch/Books/Atlas_genetics_ophtalmology.htm |
| Hereditary Ocular Disease, University of Arizona | A database of hereditary ocular diseases for patients and clinicians. | http://disorders.eyes.arizona.edu/ |
| HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) | Authority that assigns the nomenclature standards for human genes. | http://www.genenames.org/ |
| Human Genome Variation Society (HGVS) | Maintains genomic variation data and nomenclature information on sequence variants. | http://www.hgvs.org/ |
| Human Phenotype Ontology | Ontology of human phenotypic abnormalities. | http://www.human-phenotype-ontology.org/ |
| International Society for Genetic Eye Diseases & Retinoblastoma (ISGEDR) | Professional organization with a goal of promoting shared information, collaborations and the dissemination of scientific knowledge of genetic diseases of the eye and in retinoblastoma. | http://isgedr.org/ |
| London Ophthalmic Genetics Database (GENEEYE) | Comprehensive database and image library of genetic ophthalmic conditions. | http://lmdatabases.com/about_lmd.html |
| MedGen | Published material related to human medical genetics. | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/medgen/ |
| My Family Health Portrait | Tool used to create a family health history. | https://phgkb.cdc.gov/FHH/html/index.html |
| National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) | Formed as a division of the National Library of Medicine in 1988, which now serves as a central hub for providing numerous databases, tools and educational resources of biomedical information. | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ |
| National Center for Education in Maternal and Child Health's MCH Library | Online database that provides information and resources for maternal and child health. | http://www.mchlibrary.info/ |
| National Human Genome Research Institute Glossary | Contains terms and concepts used in the study of genetics for the public. | http://www.genome.gov/Glossary/ |
| National Institutes of Health Genetic Testing Registry (GTR) | Serves as a centralized location for providers to submit genetic test information. | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gtr/ |
| National Newborn Screening & Global Resource Center (NNSGRC) | Contains information on newborn screening, state contacts, general resources, and provides information sheets that describes the proper steps to follow after receiving a screening report | http://genes-r-us.uthscsa.edu/resources.htm |
| National Ophthalmic Disease Genotyping and Phenotyping Network (eyeGENE) | National Eye Institute research initiative allowing researchers access to DNA samples, clinical data, and patients interested in research. | https://www.nei.nih.gov/eyegene/ |
| National Organization for Rare Disorders (NORD) | An organization that provides support to those with rare disease by providing funding, research, education, and networking. | http://www.rarediseases.org/ |
| National Society of Genetic Counselors | An organization composed of trained genetic counselors and other health professionals dedicated to the promotion of genetic counseling. | http://www.nsgc.org/ |
| OMIM(Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man) | A database of human genes and genetic phenotypes. | http://www.omim.org/ |
| Orphanet | Provides information about rare diseases and treatments. | http://www.orpha.net/consor/cgi-bin/index.php |
| Pedigree Nomenclature | A standard used in the design of pedigrees to provide consistent information to research and health professionals as well as those in training. | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18792771 (Bennett RL et al, Standardized human pedigree nomenclature: update and assessment of the recommendations of the National Society of Genetic Counselors, J Genet Couns. 2008 Oct;17(5):424-33, doi: 10.1007/s10897-008-9169-9. Epub 2008 Sep 16) |
| PubMed | US National Library of Medicine (NLM) service that provides a search engine database of biomedical and life sciences literature citations; developed by the National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI). | http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed |
| Unique | Provides resources and support for families of children that have rare chromosome disorders | http://www.rarechromo.org/html/home.asp |
Genetic Disorders A-C
| DISORDER | EYE FINDING | MODE OF INHERITANCE | KNOWN GENES OR CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITY INVOLVED | MIM SYMBOL & NUMBER REFERENCE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABETALIPOPROTEINEMIA (BASSEN-KORNZWEIG SYNDROME) | Retinopathy | AR | MTP | #200100 |
| ACHROMATOPSIA | Photophobia, day blindness, nystagmus, colorblindness, myopia | AR | CNGA3, CNGB3 | #216900, #262300 |
| AICARDI SYNDROME | Chorioretinal lacunae, retinal detachment, cataract, nystagmus, optic nerve atrophy, optic nerve coloboma, microphthalmia, sparse lateral eyebrows | XLD | - | %304050 |
| ALAGILLE SYNDROME | Posterior embryotoxin, deep-set eyes, hypertelorism, upslanting palpebral fissures, ectopic pupils, chorioretinal atrophy, band keratopathy, cataracts, retinal pigment clumping, axenfeld anomaly, anomalous optic disc, myopia, strabismus, choroidal folds, microcornea | AD; 50-70% de novo | JAG1, NOTCH2 | #118450 |
| ALKAPTONURIA | Pigmented sclera | AR | HGD | #203500 |
| ALLAN-HERNDON-DUDLEY SYNDROME | Nystagmus, disconjugate eye movements | XLD | SLC16A2 | #300523 |
| ALPERS SYNDROME | Cortical blindness, abnormal visual evoked potential | AR | POLG | #203700 |
| ALPORT SYNDROME | Cataracts, anterior lenticonus, myopia, retinal pigmentary changes | XLD, AR | COL4A5, COL4A4, COL4A3 | #301050, #203780 |
| ALSTROM SYNDROME | Cone-rod dystrophy, photophobia, nystagmus, cataracts | AR | ALMS1 | #203800 |
| ANGELMAN SYNDROME | Refractive errors, strabismus, ocular hypopigmentation | Isolated cases | UBE3A, CDKL5, MECP2 | #105830 |
| ANIRIDIA | Cataract, glaucoma, Peter's anomaly, corneal clouding | AD | PAX6, ELP4 | #106210 |
| ANTERIOR SEGMENT MESENCHYMAL DYSGENESIS | Cataract, corneal opacity, dysgenesis of ocular anterior segment | AD | FOXE3,PITX3 | #107250 |
| APERT SYNDROME | Shallow orbits, proptosis, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures | AD | FGFR2 | #101200 |
| ARIMA SYNDROME | Chorioretinal coloboma, retinal dystrophy, nystagmus, abnormal eye movements, blepharoptosis, extinguished electroretinogram | AR | - | %243910 |
| ARMFIELD X-LINKED MENTAL RETARDATION SYNDROME | Cataracts, Glaucoma, Strabismus | XLR | - | %300261 |
| ARTS SYNDROME (MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, SYNDROMIC 18) | Optic atrophy, nystagmus | XLR | PRPS1 | #301835 |
| ATAXIA-OCULOMOTOR APRAXIA SYNDROME | Oculomotor apraxia, nystamus, hypometric saccades, external ophthalmoplegia | AR | APTX | - |
| ATAXIA TELANGIECTASIA (LOUIS-BAR SYNDROME) | Oculomotor abnormalities | AR | ATM | #208900 |
| AUTOSOMAL DOMINANT CEREBELLAR ATAXIA DEAFNESS AND NARCOLEPSY (ADCADN) | Optic atrophy | AD | DNMT1 | #604121 |
| AVELLINO CORNEAL DYSTROPHY (COMBINED GRANULAR-LATTICE CORNEAL DYSTROPHY) | Hyaline changes in anterior stroma, fusiform amyloid deposits in deeper stroma | AD | TGFBI | #607541 |
| AXENFELD-RIEGER SYNDROME | Prominent Schwalbe line, iris dysplasia, iris strands, corectopia, polycoria, glaucoma, strabismus, hypertelorism, telecanthus | AD | PITX2, FOXC1 | #180500, %601499, #602482 |
| BARAITSER-WINTER SYNDROME 1 | Coloboma, epicanthal folds, hypertelorism, ptosis | AD | ACTB | #243310 |
| BARDET BIEDL SYNDROME | Retinitis degeneration, cataracts, strabismus | AR | Numerous | Multiple |
| BASAL CELL NEVUS SYNDROME | Strabismus, glaucoma, iris coloboma, hypertelorism | AD | PTCH1, PTCH2, SUFU | #109400 |
| BEARE-STEVENSON SYNDROME | Proptosis, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures | AD | FGFR2 | #123790 |
| BECKWITH-WIEDEMANN SYNDROME | Deep-set eyes, hypertelorism, epicanthal folds, downslanting palpebral fissures, synophrys | AD, sporadic (majority of cases) | NSD1, H19, KCNQ1OT1, CDKN1C | #130650 |
| BEST MACULAR DYSTROPHY | Yellow pigmented macular lesion, cystoid macular degeneration | AD | BEST1 | #153700 |
| BIETTI CRYSTALLINE CORNEORETINAL DYSTROPHY | Retinal degeneration, choroidal vessel sclerosis, crystalline corneal deposits, marginal corneal dystrophy, night blindness | AR | CYP4V2 | #210370 |
| BLAU SYNDROME | Uveitis, choroiditis, macular and optic disc edema, band keratopathy, cataracts, glaucoma | AD | NOD2 | #186580 |
| BLEPHAROPHIMOSIS, PTOSIS, and EPICANTHUS INVERSUS (BPES) | Blepharophimosis, ptosis, epicanthus inversus, telecanthus, microphthalmia, microcornea, strabismus, hypermetropia, nystagmus, pronounced convex arched eyebrows | AD (50% de novo) | FOXL2 | #110100 |
| BLUE-CONE MONOCHROMACY | Blue cone type colorblindness, photophobia, nystagmus, myopia, macular pigment epithelial changes | XLR | OPN1LW, OPN1MW #303700 | |
| BRANCHIOOTORENAL SYNDROME | Eyes absent, lacrimal duct aplasia | AD | EYA1, SIX1, SIX5 | #113650 |
| CANTU SYNDROME | Epicanthal folds, long eyelashes | AD | ABCC9 | #239850 |
| CAT EYE SYNDROME (SCHMID-FRACCARO SYNDROME) | Iris coloboma, microphthalmia, iris malformations, cataracts, visual disturbances | Sporadic (majority), AD | sSMC of 22q11.2 | #115470 |
| CEREBRAL-CEREBELLAR-COLOBOMA SYNDROME | Chorioretinal coloboma | XLR | - | 300864 |
| CEREBROOCULOFACIOSKELETAL SYNDROME | Cataracts, blepharophimosis, microphthalmia, nystagmus, deep-set eyes | AR | ERCC6 | #214150 |
| CEREBROOCULONASAL SYNDROME | Anophthalmia, Sparse eyebrows and eyelashes, hypertelorism, epicanthal folds | AD | - | %605627 |
| CEREBROTENDINOUS XANTHOMATOSIS | Cataracts | AR | CYP27A1 | #213700 |
| CHARCOT-MARIE-TOOTH DISEASE | Glaucoma, slow pupillary reaction, nystagmus, optic nerve atrophy | AD, AR, XLD | Numerous | Multiple |
| CHARGE SYNDROME | Anophthalmia, microphthalmia, ptosis, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures, coloboma in iris, oprtic nerve, retina | AD | CHD7, SEMA3E | #214800 |
| CHEDIAK-HIGASHI SYNDROME | Decreased iris pigmentation, nystagmus, photophobia, strabismus, macular hypoplasia | AR | CHS1 | #214500 |
| CHERUBISM | Proptosis, globe displacement, lower eyelid retraction, optic neuropathy, striae of macula, marcus-gunn pupil | AD | SH3BP2 | #118400 |
| CHONDRODYSPLASIA WITH PLATYSPONDYLY, DISTINCTIVE BRACHYDACTYLY, HYDROCEPHALY, AND MICROPHTHALMIA | Microphthalmia | XLD | HDAC6 | #300863 |
| CHOROIDEREMIA | Choroidoretinal degeneration, night blindness, visual field constriction | XLD | CHM | #303100 |
| CHRISTIAN SYNDROME | Cranial nerve VI palsy | X-linked | - | #309620 |
| CHRISTIANSON SYNDROME | Ophthalmoplegia, deep-set eyes, bushy eyebrows | XLD | SLC9A6 | #300243 |
| CK SYNDROME | Strabismus, epicanthal folds, upslanting palpebral fissures, almond-shaped eyes | XLR | NSDHL | #300831 |
| COCKAYNE SYNDROME | Pigmentary retinopathy, cataracts, nystagmus, strabismus, optic atrophy, hyperopia, corneal opacity, decreased lacrimation, microphthalmos, iris hypoplasia | AR | ERCC6, ERCC8 | #216400, #133540 |
| COFFIN-SIRIS SYNDROME | Hypertelorism, myopia, strabismus, abnormal eyelash and eyebrow lengths | AD | ARID1A, ARID1B | #135900, #614607 |
| COLORBLINDNESS, DEUTAN | Green colorblindness | X-linked | OPN1MW | #303800 |
| COLORBLINDNESS, PROTAN | Red colorblindness | X-linked | OPN1LW | #303900 |
| COLORBLINDNESS, TRITANOPIC | Abnormal blue and yellow vision | AD | OPN1SW | #190900 |
| CONE-ROD DYSTROPHY | Dyschromatopsia, photophobia, nystagmus, maculopathy, progression to night blindness later | AD, AR, X-linked | Numerous | Multiple |
| CONGENITAL DISORDER OF GLYCOSYLATION | Retinitis pigmentosa, nystagmus, strabismus | AR, X-linked | Numerous | Multiple |
| CONGENITAL FIBROSIS OF EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES | Ptosis, ophthalmoplegia | AD, AR | KIF21A, PHOX2A, ARIX, TUBB3 | #135700, #602078, #600638 |
| CONGENITAL NYSTAGMUS | Pendular and horizontal nystagmus, head turn, strabismus | AD, AR, X-linked | Numerous | Multiple |
| CONGENITAL STATIONARY NIGHT BLINDNESS | Night blindness, myopia | AD, AR, X-linked | Numerous | Multiple |
| CORNEA PLANA | Hyperopia, hazy corneal limbus, corneal opacities, thin cornea | AR | KERA | #217300 |
| CORNELIA DE LANGE SYNDROME | Myopia, ptosis, synophrys, long eyelashes, hypertelorism, telecanthus, hooding of eyelids | AD, X-linked | SMC1A, HDAC8, numerous others | Multiple |
| CORPUS CALLOSUM, AGENESIS OF, WITH MENTAL RETARDATION, OCULAR COLOBOMA, AND MICROGNATHIA | Coloboma, downslanting palpebral fissures | XLR | IGBP1 | #300472 |
| COSTEFF SYNDROME | Optic atrophy | AR | OPA3 | - |
| CRIGLER-NAJJAR | GILBERT SYNDROME Jaundice | AR | UGT1A1 | #218800, #606785 |
| CROUZON SYNDROME | Shallow orbits, proptosis, strabismus, hypertelorism, optic atrophy | AD | FGFR2 | #123500 |
| CROUZON SYNDROME WITH ACANTHOSIS NIGRICANS (CROUZONODERMOSKELETAL SYNDROME) | Shallow orbits, proptosis, strabismus, hypertelorism, optic atrophy | AD | FGFR3 | #612247 |
| CUTIS LAXA, DEBRE TYPE | Strabismus, myopia, downslanting palpebral fissures | AR | ATP6V0A2 | #219200 |
| CYSTINOSIS | Photophobia, corneal and conjunctival crystals, retinopathy, recurrent corneal erosions | AR | CTNS | #219750, #219800 |
Diseases D-F
| DISORDER | EYE FINDING | MODE OF INHERITANCE | KNOWN GENES OR CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITY INVOLVED | MIM SYMBOL & NUMBER REFERENCE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DANON'S DISEASE | lenticular changes, pigmentary retinopathy, blonde fundi, myopia, ERG and visual field defects | X-linked recessive | LAMP-2 | #300257 |
| DELLEMAN SYNDROME (OCULOCEREBROCUTANEOUS SYNDROME) | Anophthalmia, microphthalmia, eyelid coloboma, orbital cysts, nystagmus | Isolated cases | - | 164180 |
| DOWN SYNDROME | Iris brushfield spots, upslanting palpebral fissures, epicanthal folds | Most cases not inherited | Trisomy 21 (most cases), translocation, mosaic | #190685 |
| DOYNE HONEYCOMB DYSTROPHY (MALATTIA LEVENTINESE) | Retinal degeneration | AD | EFEMP1 | #126600 |
| DUANE-RADIAL RAY SYNDROME | Strabismus, Duane anomaly, globe retraction and palpebral fissure narrowing on adduction, optic disc hypoplasia, iris coloboma, retinal coloboma, epicanthal folds, hypertelorism, cataracts, microphthalmia | AD | SALL4 | #607323 |
| DYSKERATOSIS CONGENITA | Sparse eyelashes, optic atrophy, conjunctival leukoplakia, epiphora, strabismus, cataract | AD, AR, X-linked | Numerous | Multiple |
| ECTOPIA LENTIS ET PUPILLAE | Ectopic lens and pupil, cataract, myopia, abnormal appearing iris, increased corneal diameter, retinal detachment | AR | ADAMTSL4 | #225200 |
| ECTOPIA LENTIS, FAMILIAL | Congenital lens dislocation | AD | FBN1 | #129600 |
| ECTOPIA LENTIS, ISOLATED | Lens dislocation | AR | ADAMTSL4 | #225100 |
| EHLERS-DANLOS SYNDROME | Myopia, ectopia lentis, blue sclera, epicanthal folds, keratoconus | AD | COL5A1 and COL5A2, COL3A1, TNXB | Multiple |
| ENHANCED S-CONE SYNDROME | Vitreoretinal degeneration, retinoschisis, hemeralopia, macular edema, cataract, night blindness | AR | NR2E3 | #268100 |
| EPITHELIAL BASEMENT MEMBRANE CORNEAL DYSTROPHY (MAP-DOT-FINGERPRINT CORNEAL DYSTROPHY) | Map lines-dots-fingerprint lines epithelial corneal changes, recurrent corneal erosions | AD | TGFBI | #121820 |
| FABRY DISEASE (HEREDITARY DYSTOPIC LIPIDOSIS) | Corneal opacities (cornea verticillata), retinal vessel tortuosity, cataracts | X-linked | GLA | #301500 |
| FAMILIAL DYSAUTONOMIA | Alacrima, Diminished corneal reflex | AR | IKBKAP | #223900 |
| FISH-EYE DISEASE | Corneal opacities | AR | LCAT | #136120 |
| FUCH'S ENDOTHELIAL CORNEAL DYSTROPHY | Corneal endothelial guttata, stromal edema, endothelial cell death, hypertrophy and polymorphism | AD | Numerous | Multiple |
Diseases G-I
| DISORDER | EYE FINDING | MODE OF INHERITANCE | KNOWN GENES OR CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITY INVOLVED | MIM SYMBOL & NUMBER REFERENCE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GALACTOKINASE DEFICIENCY | Cataracts | AR | GALK1 | #230200 |
| GALACTOSEMIA | Cataracts | AR | GALT | #230400 |
| GAUCHER'S DISEASE | Macular atrophy, increased vascular permeability, perimacular grayness, brown deposits at limbus, white deposits in anterior segment, strabismus, oculomotor apraxia, supranuclear gaze palsy, hypertelorism, corneal opacities, nystagmus | AR | GBA | #230800, #230900, #231000, #231005, #608013 |
| GLAUCOMA, CONGENITAL | Buphthalmos, increased intraocular pressure, corneal haze, myopia | AR | CYP1B1, MYOC | #231300, %600975 |
| GLAUCOMA, OPEN ANGLE JUVENILE ONSET | Increased intraocular pressure, myopia | AD | MYOC, CYP1B1 | #137750 |
| GLAUCOMA, OPEN ANGLE ADULT ONSET | Increased intraocular pressure, myopia | AD | OPTN, ASB10, WDR36 | #137760, %601682, %602429, #603383, #609887, %611276, #177700 |
| GM1-GANGLIOSIDOSIS, TYPE I | Cherry-red spot, hypertelorism | AR | GLB1 | #230500 |
| GM1-GANGLIOSIDOSIS, TYPE II | Optic atrophy | AR | GLB1 | #230600 |
| GM1-GANGLIOSIDOSIS, TYPE III | Corneal clouding | AR | GLB1 | #230650 |
| GOLDENHAR SYNDROME (HEMIFACIAL MICROSOMIA) | Upper eyelid coloboma, epibulbar dermoid, blepharophimosis, strabismus, microphthalmia, anophthalmia | AD | - | %164210 |
| GOLTZ SYNDROME | Microphthalmia, anophthalmia, strabismus, coloboma, aniridia, ectopia lentis, optic atrophy, nystagmus | XLD | PORCN | #305600 |
| GRANULAR CORNEAL DYSTROPHY (GROENOUW TYPE I) | Opacities in stromal layer | AD | TGFBI | #121900 |
| GYRATE ATROPHY | Progressive chorioretinal degeneration, night blindness, myopia, cataracts | AR | OAT | #258870 |
| HEREDITARY HEMORRHAGIC TELANGIETASIA (OSLER-RENDU-WEBER DISEASE) | Conjunctival telangiectases | AD | ENG | #187300 |
| HERMANSKY-PUDLAK SYNDROME | Oculocutaneous albinism, nystagmus, reduced iris pigment, decreased retinal pigment, foveal hypoplasia | AR | Numerous | Multiple |
| HOMOCYSTINURIA | Ectopia lentis, myopia, glaucoma | AR | CBS | #236200 |
| IFAP SYNDROME WITH OR WITHOUT BRESHECK SYNDROME | Photophobia, corneal opacities and erosions, vascularizing keratitis | XLR | MBTPS2 | #308205 |
| INCONTINENTIA PIGMENTI (BLOCH-SULZBERGER SYNDROME) | Retinal vascular proliferation, retinal detachment, strabismus, optic atrophy, cataract, microphthalmos | XLD | IKBKG | #308300 |
Diseases J-L
| DISORDER | EYE FINDING | MODE OF INHERITANCE | KNOWN GENES OR CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITY INVOLVED | MIM SYMBOL & NUMBER REFERENCE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| JACKSON-WEISS SYNDROME | Craniosynostosis | AD | FGFR1, FGFR2 | #123150 |
| JALILI SYNDROME | Cone-rod dystrophy, nystagmus, photophobia, bull's eye macular lesion, progressive central vision loss, night blindness, optic pale disc | AR | CNNM4 | #217080 |
| JOUBERT SYNDROME | Pigmentary retinopathy, oculomotor apraxia or difficulty in smooth visual pursuits and jerkiness in gaze tracking, ptosis, coloboma, epicanthal folds | AR (most common), XLR | Numerous | Multiple |
| JUBERG-MARSIDI SYNDROME | Ptosis, epicanthal folds, hypertelorism, upslanting palpebral fissures, exotropia, optic atrophy | XLR | ATRX | #309580 |
| KRABBE DISEASE | Nystagmus, optic atrophy | AR | GALC | #245200 |
| KEARNS-SAYRE SYNDROME | Ptosis, progressive external ophthalmoplegia, pigmentary retinopathy | Mitochondrial | Multiple | #530000 |
| KLIPPEL-TRENAUNAY-WEBER | Glaucoma | Isolated cases | - | %149000 |
| LATTICE CORNEAL DYSTROPHY | Lattice pattern of amyloid deposits in stromal layer, recurrent corneal erosions | AD | TGFBI | #122200, #608471 |
| LCHAD (LONG-CHAIN 3-HYDROXYACYL-CoA DEHYDROGENASE) DEFICIENCY | Pigmentary retinopathy | AR | HADHA | #609016 |
| LEBER CONGENITAL AMAUROSIS | Pigmentary retinopathy, photophobia, cataract, nystagmus, eye poking, diminished electroretinogram | AD, AR | Numerous | Multiple |
| LEBER HEREDITARY OPTIC NEUROPATHY | Progressive blurred vision, optic atrophy, vascular tortuosity of central retinal vessels, circumpapillary telangiectatic macroangiopathy, retinal nerve fibers swelling | Mitochondrial | MTND1, MTND4, MTND5, MTND6 | #535000 |
| LEIGH SYNDROME | Pigmentary retinopathy, nystagmus, optic atrophy, ophthalmoplegia | Mitochondrial | Numerous | Multiple |
| LOEYS-DIETZ SYNDROME (LDS) | Mild myopia, strabismus, exotropia, amblyopia, decreased corneal thickness, keratoconus, cornea plana, cataracts, blue sclerae, ectopia lentis (rarely), retinal tortuosity, retinal detachment
Specific LDS mutations causing glaucoma, high myopia, and corneal guttata have been identified |
AD, de novo | TGFBR1, TGFBR2, SMAD2, SMAD3, TGFB2, and TGFB3 | #609192 |
| LOWE | Glaucoma, congenital cataracts, microphthalmia | XLR | OCRL1 | #309000 |
Diseases M-O
| DISORDER | EYE FINDING | MODE OF INHERITANCE | KNOWN GENES OR CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITY INVOLVED | MIM SYMBOL & NUMBER REFERENCE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MACULAR DEGENERATION, AGE-RELATED | Degeneration of macula that affects central vision | - | Numerous | Multiple |
| MACULAR CORNEAL DYSTROPHY (GROENOUW TYPE II) | Gray-white punctate opacities in stromal layer that extent to peripheral cornea with lack of clear spaces between opacities | AR | CHST6 | #217800 |
| MAINZER-SALDINO SYNDROME | Retinal pigmentary dystrophy, nystagmus | AR | IFT140 | #266920 |
| MANNOSIDOSIS | Conjunctival vessel tortuosity, nystagmus, impaired smooth pursuits, progressive retinal degeneration, heavy eyebrows, epicanthal folds | AR | MANBA, MAN2B1 | #248510, #248500 |
| MARCUS GUNN PHENOMENON | Unilateral congenital ptosis, elevation of ptotic lid upon movement of lower jaw | ?AD | - | 154600 |
| MARFAN SYNDROME | Ectopia lentis, myopia | AD | FBN1 | #154700 |
| MASS SYNDROME (OVERLAP CONNECTIVE TISSUE DISEASE) | Myopia | - | FBN1 | #604308 |
| MECKEL SYNDROME | Iris colobma, hypertelorism and hypotelorism, microphthalmia | AR | Numerous | Multiple |
| MEESMANN CORNEAL DYSTROPHY | Punctate opacities in corneal epithelium, photophobia, astigmatism | AD | KRT3, KRT12 | #122100 |
| MELAS SYNDROME | Cortical blindness, hemianopsia, cataracts | Mitochondrial | Multiple | #540000 |
| MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA AND DISTINCTIVE FACIAL APPEARANCE | Strabismus, nystagmus, hypotelorism, deep-set eyes | XLR | OPHN1 | #300486 |
| MERRF SYNDROME | Optic atrophy, pigmentary retinopathy | Mitochondrial | Numerous | #545000 |
| METACHROMATIC LEUKODYSTROPHY | Optic atrophy | AR | ARSA | #250100 |
| MICPCH SYNDROME | Epicanthal folds, hypertelorism, optic nerve hypoplasia, strabismus | XLD | CASK | #300749 |
| MOHR-TRANEBJAERG SYNDROME | Cortical blindness, myopia, photophobia, constricted visual fields | XLR | TIMM8A | #304700 |
| MOYAMOYA DISEASE | Morning glory disc anomaly, choroidal coloboma | AR | Numerous | Multiple |
| MOYAMOYA DISEASE, SYNDROMIC | Ptosis, cataracts, hypertelorism, deep-set eyes | XLR | Deletion of Xq28 | #300845 |
| MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE IH (HURLER SYNDROME) | Corneal clouding, retinopathy, glaucoma | AR | IDUA | #607014 |
| MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE IH/S (HURLER-SCHEIE SYNDROME) | Corneal clouding | AR | IDUA | #607015 |
| MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE IS (SCHEIE SYNDROME) | Corneal clouding, retinopathy, glaucoma | AR | IDUA | #607016 |
| MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE II (HUNTER SYNDROME) | Retinopathy, ptosis, papilledema | XLR | IDS | #309900 |
| MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE IIIA (SANFILIPPO SYNDROME A) | Synophrys | AR | SGSH | #252900 |
| MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE IIIB (SANFILIPPO SYNDROME B) | Synophrys | AR | NAGLU | #252920 |
| MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE IIIC (SANFILIPPO SYNDROME C) | Retinitis pigmentosa, synophrys | AR | HGSNAT | #252930 |
| MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE IIID (SANFILIPPO SYNDROME D) | Synophrys | AR | GNS | #252940 |
| MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE IVA (MORQUIO SYNDROME A) | Corneal clouding, Retinopathy | AR | GALNS | #253000 |
| MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE IVB (MORQUIO SYNDROME B) | Corneal clouding, Retinopathy | AR | GLB1 | #253010 |
| MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE VI (MAROTEAUX-LAMY SYNDROME) | Corneal clouding, glaucoma | AR | ARSB | #253200 |
| MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE VII (SLY SYNDROME) | Corneal clouding | AR | GUSB | #253220 |
| MUENKE SYNDROME | Ptosis, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures | AD | FGFR3 | #602849 |
| MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY-DYSTROGLYCANOPATHY | Microphthalmia, microcornea, colobomas, optic nerve hypoplasia, cataracts, retinal dysplasia, iris malformation, myopia, glaucoma | AD, AR (most) | Numerous | Multiple |
| MYOTONIC DYSTROPHY | Iridescent cataract | AD | DMPK, ZNF9, CNBP | #160900, #602668 |
| NAIL-PATELLA SYNDROME | Cataract, microcornea, microphakia, keratoconus, glaucoma, ptosis | AD | LMX1B | #161200 |
| NANCE-HORAN SYNDROME | Congenital cataracts, glaucoma, microphthalmia, microcornea, nystagmus | XLD | NHS | #302350 |
| NATIVE AMERICAN MYOPATHY | Short and downslanting palpebral fissures, ptosis, telecanthus | AR | STAC3 | #255995 |
| NEUROFIBROMATOSIS TYPE I | Café au lait, optic glioma, lisch nodules, glaucoma | AD | NF1 | #162200 |
| NEUROFIBROMATOSIS Type II | Cataracts, retinal hamartoma | AD | NF2 | #101000 |
| NEUROFIBROMATOSIS-NOONAN SYNDROME | Ptosis, lisch nodules, epicanthal folds, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures | AD | NF1 | #601321 |
| NEUROPATHY, ATAXIA, AND RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA (NARP) | Retinopathy, nystagmus, sluggish pupils | Mitochondrial | MT-ATP6 | #551500 |
| NIEMANN-PICK DISEASE | Cherry-red macula, granular appearing macula, vertical supranuclear gaze palsy | AR | NPC1, NPC2, SMPD1 | #257200, #607616, #257220 |
| NOONAN SYNDROME | Epicanthal folds, myopia, ptosis, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures | AD | Numerous | Multiple |
| NORMAL-TENSION GLAUCOMA | Glaucoma with no elevated intraocular pressure | - | OPA1, OPTN | #606657 |
| NORRIE DISEASE | Retinal detachment, microphthalmia, retinal dysplasia, corneal and vitreous opacities, cataract, optic atrophy | XLR | NDP | #310600 |
| NEURONAL CEROID LIPOFUSCINOSIS | Optic atrophy, retinal degeneration, abnormal electroretinogram | AD, AR (majority) | Numerous | Multiple |
| OCCULT MACULAR DYSTROPHY | Progressive decreased vision, reduced focal macular electroretinogram | AD | RP1L1 | #613587 |
| OCULAR ALBINISM | Nystagmus, decreased iris pigment, translucent iris, foveal hypoplasia, strabismus, translucent iris, photophobia, high refractive erros | X-linked | GPR143 | #300500 |
| OCULOCUTANEOUS ALBINISM | Nystagmus, decreased iris pigment, translucent iris, foveal hypoplasia, strabismus, white hair and skin, translucent iris, photophobia, high refractive erros | AR | TYR, OCA2, TYRP1, or SLC45A2, MC1R | Multiple |
| OCULOPHARYNGEAL MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY | Progressive blepharoptosis beginning most often in the 5th decade of life, facial muscle weakness, eye motility disorders | AD, AR | PABN1; an expansion of alanine (GCN) on the repeat region on chromosome 14q11.2 | #164300 |
| OGUCHI DISEASE | Congenital stationary night blindness, golden yellow fundus in light that disappears in dark adaptation (Mizuo-Nakamura phenomenon) | AR | SAG, GRK1 | #258100, #613411 |
| OPTIC ATROPHY | Optic nerve pallor, cataract | AD, AR, X-linked | Numerous | Multiple |
| ORAL-FACIAL-DIGITAL SYNDROME | Downslanting palpebral fissures, telecanthus, hypertelorism, epicanthus, nystagmus, strabismus | AR, XLD | Numerous | Multiple |
| OSTEOGENESIS IMPERFECTA | Blue or grey sclera | AD (most common), AR, sporadic | COL1A1, COL1A2, CRTAP, LEPRE1 | Multiple |
Diseases P-R
| DISORDER | EYE FINDING | MODE OF INHERITANCE | KNOWN GENES OR CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITY INVOLVED | MIM SYMBOL & NUMBER REFERENCE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PELIZAEUS-MERZBACHER | Optic atrophy, nystagmus | XLR | PLP1 | #312080 |
| PETERS' ANOMALY | Central corneal leukoma, absent Descemet membrand and posterior stroma, iris and lens attachments to posterior cornea | AD, AR | PAX6, PITX2, CYP1B1, FOXC1 | #604229 |
| PETERS-PLUS SYNDROME (KRAUSE-KIVLIN SYNDROME) | Peter's anomaly, nystagmus, glaucoma, cataract, myopia, coloboma, upslanting palpebral fissures, ptosis, hypertelorism | AR | B3GALTL | #261540 |
| PFEIFFER SYNDROME | Shallow orbits, proptosis, hypertelorism, downslanting palpebral fissures, strabismus | AD | FGFR1, FGFR2 | #101600 |
| PHACE ASSOCIATION | Optic nerve hypoplasia, microphthalmos, exophthalmos, choroidal hemangiomas, colobomas, cryptophthalmos, strabismus, posterior embryotoxon, Horner syndrome, strabismus, cataracts | - | - | 606519 |
| PHENYLKETONURIA | Possible cataracts and blue eyes in untreated | AR | PAH | #261600 |
| PIERRE ROBIN SEQUENCE | Stickler syndrome | AD, AR, X-linked, isolated | - | %261800 |
| PIGMENT DISPERSION SYNDROME | Glaucoma, myopia, pigment granules on corneal endothelium, iris transillumination defects, concave iris, increased pigmentation of trabecular meshwork, deposited pigment on Schwalbe's line | AD | - | %600510 |
| PORETTI-BOLTSHAUSER SYNDROME | Strabismus, cataracts, high myopia, retinal thinning, retinal avascularity, neovascularization, retinal detachment | AR | LAMA1 | #615960 |
| PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME | Refractive errors, strabismus, upslanting palpebral fissures, almond-shaped eyes | Isolated | NDN, SNRPN | #176270 |
| PRIETO SYNDROME | Strabismus, ptosis, nystagmus, hypertelorism, epicanthal folds | XLR | - | %309610 |
| PROUD SYNDROME | Nystagmus, strabismus, optic atrophy, synophrys | X-linked | ARX | #300004 |
| PSEUDOEXFOLIATION SYNDROME | Glaucoma, white flaky deposits on anterior lens and pupillary border of iris, iris transillumination defects, pigmented granules on trabecular meshwork, poor pupillary response in dilation, weak zonules | AD | LOXL1 | #177650 |
| REFSUM DISEASE | Night blindness, cataracts, retinal pigmentary degeneration, constricted visual fields | AR | PHYH, PEX7 | #266500 |
| REIS-BUCKLERS CORNEAL DYSTROPHY | Reticular opacities in Bowman's layer, recurrent corneal erosions | AD | TGFBI | #608470 |
| RENPENNING SYNDROME (MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, RENPENNING TYPE) | Strabismus, cataracts, epicanthus, colobomas, microphthalmia, long eyelashes, sparse eyebrows, hyperopia, upslanting palpebral fissures | XLR | PQBP1 | #309500 |
| RETINITIS PIGMENTOSA | Progressive retinal degeneration, night blindness, constricted visual fields, dyschromatopsia, cystoid macular edema, pigment clumps in retina, attenuated retinal vessels, waxy pallor of optic disc, cataracts | AD, AR, XLR | Numerous | Multiple |
| RETINOBLASTOMA | Leukcoria, strabismus, retinal detachment, glaucoma, pseudouveitis, proptosis, hyphema, orbital cellulitis, red painful eye | AD, sporadic | RB1 | #180200 |
| RETINOSCHISIS, JUVENILE X LINKED | Retinoschisis, retinal detachment, nystagmus, vitreous hemorrhage, cystic maculopathy X-linked | RS1 | #312700 | |
| ROIFMAN SYNDROME | Retinal dystrophy, strabismus, refractive error, narrow palpebral fissures, downslanting palpebral fissures, long eyelashes | XLR | - | %300258 |
| RUBINSTEIN-TAYBI SYNDROME | Glaucoma, cataracts, strabismus, coloboma, epicanthal folds, ptosis, downward slanting palpebral fissures, heavy and arched eyebrows, long eyelashes | AD | CREBBP, EP300 | #180849, #613684, #610543 |
| RUSSELL-SILVER SYNDROME | Blue sclera | AD, AR, sporadic (most cases) | #180860 |
Diseases S-U
| DISORDER | EYE FINDING | MODE OF INHERITANCE | KNOWN GENES OR CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITY INVOLVED | MIM SYMBOL & NUMBER REFERENCE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SAETHRE-CHOTZEN SYNDROME | Coronal synostosis, orbital asymmetry, shallow orbits, ptosis, strabismus, hypertelorism, lacrimal duct abnormalities | AD | TWIST1, FGFR2 | #101400 |
| SANDHOFF DISEASE (GM2-GANGLIOSIDOSIS, TYPE II) | Cherry red spot | AR | HEXB | #268800 |
| SCHNYDER CORNEAL DYSROPHY | Corneal clouding in stroma yellow-white crystal deposits | AD | UBIAD1 | #121800 |
| SENGERS SYNDROME | Cataract, strabismus, glaucoma, myopia | AR | AGK | #212350 |
| SENIOR-LOKEN SYNDROME | Tapetoretinal degeneration, photophobia, nystagmus, hyperopia, flat electroretinogram | AR | NPHP1, NPHP4 SDCCAG8, WDR19, CEP290, IQCB1 | Multiple |
| SEPTIC-OPTIC DYSPLASIA (DE MORSIER SYNDROME) | Optic nerve hypoplasia, nystagmus | AD, AR, sporadic | HESX1, OTX2, SOX2 | #182230 |
| SHASHI X-LINKED MENTAL RETARDATION SYNDROME (MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, SYNDROMIC 11) | Narrow palpebral fissures, periorbital fullness | XLR | - | %300238 |
| SCHIMKE X-LINKED MENTAL RETARDATION SYNDROME | External ophthalmoplegia | X-linked | - | 312840 |
| SMITH-MAGENIS SYNDROME (CHROMOSOME 17p11.2 DELETION SYNDROME) | Microcornea, strabismus, iris anomalies, myopia | AD (sporadic unless secondary to a parental balanced translocation) | RAI1, most cases caused by by a 3.7-Mb interstitial deletion in chromosome 17p11.2 | #182290 |
| SICKLE CELL ANEMIA | Retinopathy, retinal and vitreous hemorrhages, tractional retinal detachments, retinal vascular occlusions, comma shaped vessels in conjunctiva, angioid streaks | AR | HBB | #603903 |
| SIMPSON-GOLABI-BEHMEL SYNDROME | Hypertelorism, epicanthal folds, downslanting palpebral fissures | XLR | GPC3, OFD1 | #312870, #300209 |
| SORSBY FUNDUS DYSTROPHY | Progressive macular dystrophy, Night blindness | AD | TIMP3 | #136900 |
| SPASTIC PARAPLEGIA | Nystagmus, optic atrophy | AD, AR, X-linked, Mitochondrial | Numerous | Multiple |
| SPINOCEREBELLAR ATAXIA, X-LINKED 1 | Slow eye movements, strabismus | XLR | ATP2B3 | #302500 |
| STARGARDT DISEASE/FUNDUS FLAVIMACULATUS | Progressive macular dystrophy, central retinal atrophy, macular flecks, later disease onset and scattered flecks with Fundus Flavimaculatus | AD, AR | ABCA4 (majority cases), ELOVL4, PROM1 | #248200, #600110, #603786 |
| STICKLER SYNDROME | Myopia, retinal detachment, cataracts, glaucoma, vitreoretinal degeneration, no ocular signs (type III) | AD (Type I,II,III), AR (Type IV, V) | COL2A1, COL11A1, COL11A2, COL9A1, COL9A2 | #108300, #604841, #184840, #614134, #614284, #609508 |
| STURGE-WEBER SYNDROME | Choroidal hemaiomata, glaucoma | Isolated cases | GNAQ | #185300 |
| SULFOCYSTEINURIA (SULFITE OXIDASE DEFICIENCY) | Ectopia lentis | AR | SUOX | #272300 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 1 (LENZ MICROPHTHALMIA SYNDROME) | Anophthalmia, microphthalmia, microcornea, ptosis, colobomas | X-linked | NAA10 | #309800 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 2 (OCULOFACIOCARDIODENTAL SYNDROME) | Microphthalmia, microcornea, cataract, thick eyebrows, ptosis, bleparophimosis, strabismus | XLD | BCOR | #300166 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 3 (MICROPHTHALMIA AND ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA SYNDROME) | Anophthalmia, microphthalmia, coloboma, optic nerve hypoplasia | AD | SOX2 | #206900 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 4 | Anophthalmia, ankyloblepharon | X-linked | - | %301590 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 5 | Anophthalmia, microphthalmia, microcornea, retinal dystrophy, optic nerve hypoplasia, colobomas | AD | OTX2 | #610125 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 6 | Anophthalmia, microphthalmia | AD | BMP4 | #607932 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 7 (MIDAS SYNDROME) | Microphthalmia, cataracts, coloboma, sclerocornea, pigmentary retinopathy | XLD | HCCS | #309801 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 8 | Microphthalmia, Microcornea, short palpebral fissures | AD | - | %601349 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 9 (MATTHEW-WOOD SYNDROME) | Anophthalmia, microphthalmia, coloboma, optic nerve hypoplasia, blepharophimosis, broad eyebrows | AR | STRA6 | #601186 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 10 | Microphthalmia | - | - | %611222 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 11 | Microphthalmia, optic nerve hypoplasia | AR | VAX1 | #614402 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 12 | Anophthalmia, microphthalmia | AD | RARB | #615524 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 13 | Microphthalmia, microcornea, ptosis, coloboma, nystagmus, esotropia | X-linked | HMGB3 | #300915 |
| SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 14 | Microphthalmia, coloboma | - | MAB21L2 | #615877 |
| TARP SYNDROME | Short palpebral fissures, optic atrophy, underdeveloped supraorbital ridges, hypertelorism | XLR | RBM10 | #311900 |
| TAY-SACHS DISEASE (GM2-GANGLIOSIDOSIS, TYPE I) | Cherry red spot | AR | HEXA | #272800 |
| THIEL-BEHNKE CORNEAL DYSTROPHY | Honeycomb-shaped opacities in Bowman's layer, recurrent corneal erosions | AD | TGFBI | %602082 |
| TREACHER COLLINS SYNDROME | Downslanting palpebral fissures, lower eyelid colobomas | AD, AR | Numerous | #154500, #613717, #248390 |
| TUBEROUS SCLEROSIS | Retinal hamartomas, adenoma sebaceum of eyelids | AD (2/3 de novo) | TSC1 and TSC2 | #191100, #613254 |
| TURNER SYNDROME | Hypertelorism, Ametropia, keratoconus, strabismus, epicanthal folds, anterior segment dysgenesis | Most not inherited, nondisjunction of X chromosome | SHOX | - |
| TYROSINEMIA, TYPE II | Herpetiform corneal ulcers, photophobia, excessive tearing | AR | TAT | #276600 |
| USHER SYNDROME | retinitis pigmentosa, cataracts | AR | 11 genes, majority of cases due to MYO7A, USH2A | Multiple |
Diseases V-Z
| DISORDER | EYE FINDING | MODE OF INHERITANCE | KNOWN GENES OR CHROMOSOMAL ABNORMALITY INVOLVED | MIM SYMBOL & NUMBER REFERENCE |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| VACTERL ASSOCIATION WITH HYDROCEPHALUS | Downward gaze of eyes | Mostly sporadic | PTEN | #276950 |
| VAN DEN BOSCH SYNDROME | Choroideremia | XLR | - | %314500 |
| VITELLIFORM MACULAR DYSTROPHY, ADULT-ONSET | Yellow pigmented macular lesion, choroidal neovascularization, central retinal pigment epithelium atrophy | AD | PRPH2, BEST1 | #608161 |
| VON HIPPEL-LINDAU SYNDROME | Hemangioblastoma | AD | VHL | #193300 |
| WAARDENBURG SYNDROME | Heterochromic irides, dystrophia canthorum, blepharophimosis, hypertelorism, blue irides, synophrys | AD, AR | EDN3, EDNRB, MITF, PAX3, SNAI2, SOX10 | Multiple |
| WAGNER SYNDROME | Myopia, vitreoretinal degeneration, chorioretinal atrophy, glaucoma, retinal detachment | AD | VCAN | #143200 |
| WATSON SYNDROME | Lisch nodules | AD | NF1 | #193520 |
| WEILL-MARCHESANI SYNDROME | Ectopia lentis, microspherophakia, glaucoma, myopia, cataract, shallow anterior chamber | AD, AR | ADAMTS10, FBN1, LTBP2 | #277600, #608328, #614819 |
| WIEACKER-WOLFF SYNDROME | Ptosis, upslanting palpebral fissures, oculomotor apraxia | XLR | ZC4H2 | #314580 |
| WIILIAMS SYNDROME (WILLIAMS-BEUREN SYNDROME) | strabismus, stellate iris pattern of the anterior stroma, and retinal vessel tortuosity | AD | ELN 7q11.23 | 194050 |
| WILSON DISEASE | Kayser-Fleischer ring, cataracts | AR | ATP7B | #277900 |
| WITTWER SYNDROME | Microphthalmia, optic atrophy | X-linked | - | %300421 |
| WOLFRAM SYNDROME | Pigmentary retinopathy, optic atrophy, nystagmus, ptosis | AR | WFS1, CISD2 | #222300, #604928, #598500 |
| XERODERMA PIGMENTOSUM | Keratitis, microcephaly, neoplasms, photophobia | AR | XPA, XPC, ERCC2, ERCC3, POLH | Multiple |
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Genetics Home Reference Glossary, World Wide Web URL: http://ghr.nlm.nih.gov/glossary
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 Hartwell, L. (2004). Genetics: From genes to genomes (2nd ed.). Boston, Mass.: McGraw-Hill Higher Education.
- ↑ 3.0 3.1 Mayo Clinic Health Information, World Wide Web URL: http://www.mayoclinic.org/
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 National Human Genome Research Institute, World Wide Web URL: https://www.genome.gov/
- ↑ Karthikeyan A. Sadagopan, Jenina Capasso, and Alex V. Levin, Genetics for the ophthalmologist, Oman J Ophthalmol. 2012 Sep-Dec; 5(3): 144–149, doi: 10.4103/0974-620X.106092, PMCID: PMC3574508
- ↑ Jenina E. Capasso, The Cost of Genetic Testing for Ocular Disease, Curr Opin Ophthalmol. 2014;25(5):394-399
- ↑ Edwin M. Stone, MD, Ph.D., Anthony J. Aldave, MD, Arlene V. Drack, MD et al., Recommendations for Genetic Testing of Inherited Eye Diseases, 2012 American Academy of Ophthalmology
- ↑ Hennekam RC, Biesecker LG, Allanson JE, et al., Elements of Morphology Consortium. 2013. Elements of morphology: General terms for congenital anomalies. Am J Med Genet Part A 161A:2726–2733.
- ↑ Mona Al-Enezi, MD, FRCS (Ed), Hanan Al-Saleh, MD, FRCS, and Murad Nasser, MS (ICO), FRCS (Ed), Mitochondrial Disorders with Significant Ophthalmic Manifestations, Middle East Afr J Ophthalmol. 2008 Apr-Jun; 15(2): 81–86, doi: 10.4103/0974-9233.51998
- ↑ American College of Medical Genetics, World Wide Web URL: https://www.acmg.net
- ↑ Jane L Ashworth FRCOphth, PhD, Friedrich E Kruse MD, Björn Bachmann MD et al., Ocular manifestations in the mucopolysaccharidoses – a review, Clinical & Experimental Ophthalmology Special Issue: Mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) and The Eye: What do we know and how can we treat? Volume 38, Issue Supplement s1, pages 12–22, August 2010
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM®. McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine, Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, MD), World Wide Web URL: http://omim.org/
- ↑ NCBI Gene Reviews Rare Disease Database, World Wide Web URL: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK1116/
- ↑ NORD Rare Disease Information Rare Disease Database, World Wide Web URL: https://www.rarediseases.org/rare-disease-information/rare-diseases
- ↑ M Rajappa, A Goyal and J Kaur, Inherited metabolic disorders involving the eye: a clinico-biochemical perspective, Eye (2010) 24, 507–518; doi:10.1038/eye.2009.229; published online 2 October 2009
- ↑ Roger E. Stevenson, MD, Charles E. Schwartz, Ph.D, R. Curtis Rogers, MD, Atlas of X-Linked Intellectual Disability Syndromes, Second Edition, 2012 Oxford University Press
- ↑ Elias I. Traboulsi, MD, Genetic Diseases of the Eye, Second Edition, Oxford University Press, 2012
- ↑ Myron Yanoff, Jay S. Duker, Ophthalmology Second Edition, 2004, Mosby, Inc.