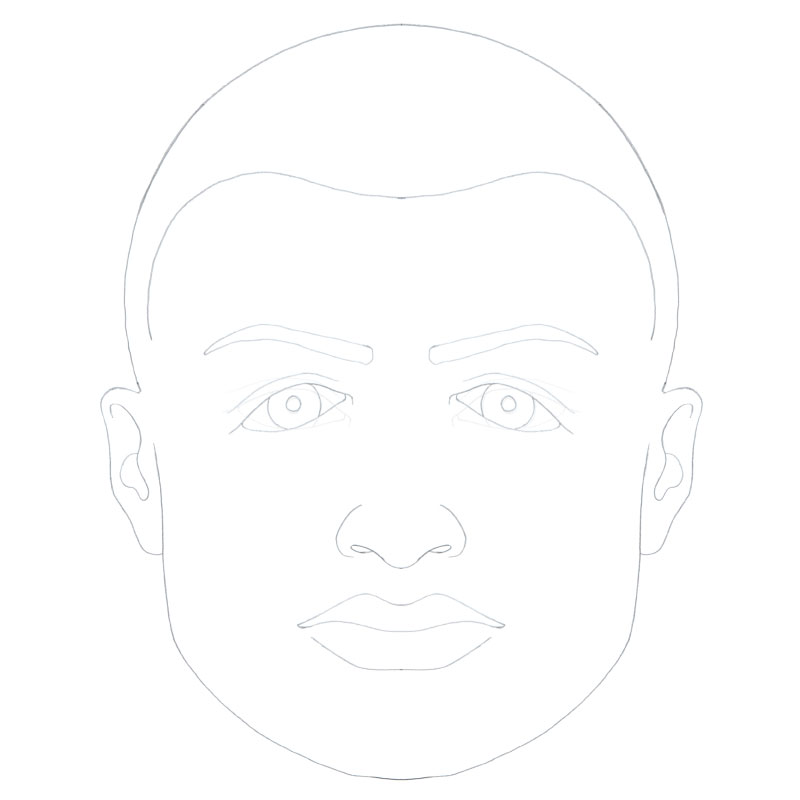
Dysmorphology of the Eye and Periorbital Region
All content on Eyewiki is protected by copyright law and the Terms of Service. This content may not be reproduced, copied, or put into any artificial intelligence program, including large language and generative AI models, without permission from the Academy.
Introduction
Although there is a wide variation of the facial dimensions between ethnicity, gender, and age, careful inspection and selective objective measurements obtained as part of the clinical exam may reveal parameters outside normal standards, which may assist in narrowing a differential diagnosis and ultimately making a diagnosis. Depicted in the following sections are periorbital dimensions along with described growth patterns presented in a tabular format [1] [2] [3] [4] [5] [6] [7], followed by selected dysmorphological entities with examples of associated conditions [8] [9] [10] [11] [12].
Periorbital Dimensions
Definitions
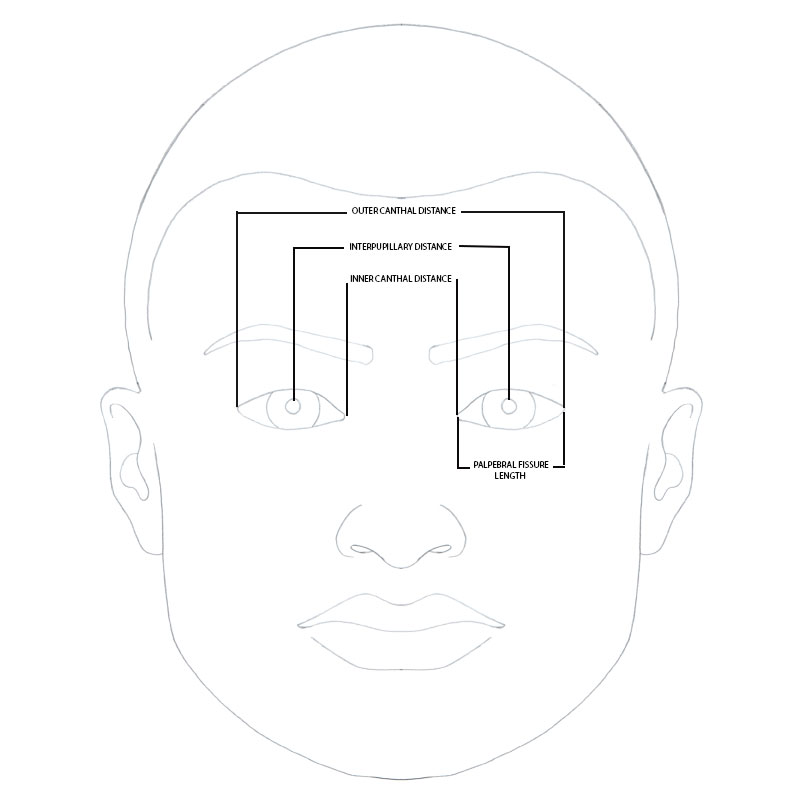
- Outer canthal distance: distance between the lateral canthi of the eyes
- Inner canthal distance: distance between the medical canthi of the eyes
- Interpupillary distance: distance between the pupil centers of the eyes
- Palpebral fissure length: distance between the inner and outer canthi of the eye; the actual palpebral fissure encompasses the exposed area between the top and bottom eyelids. The adult palpebral fissure is typically about 3 cm horizontally and 0.8 to 1.1 cm vertically.
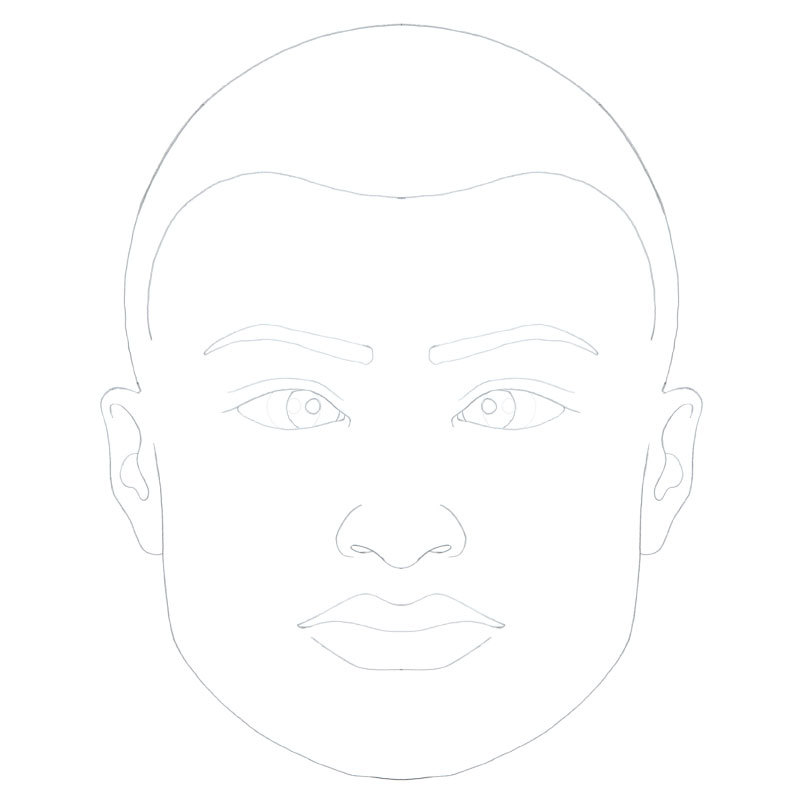
Schematic
Figure 1. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting select periorbital dimensions. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Growth parameters
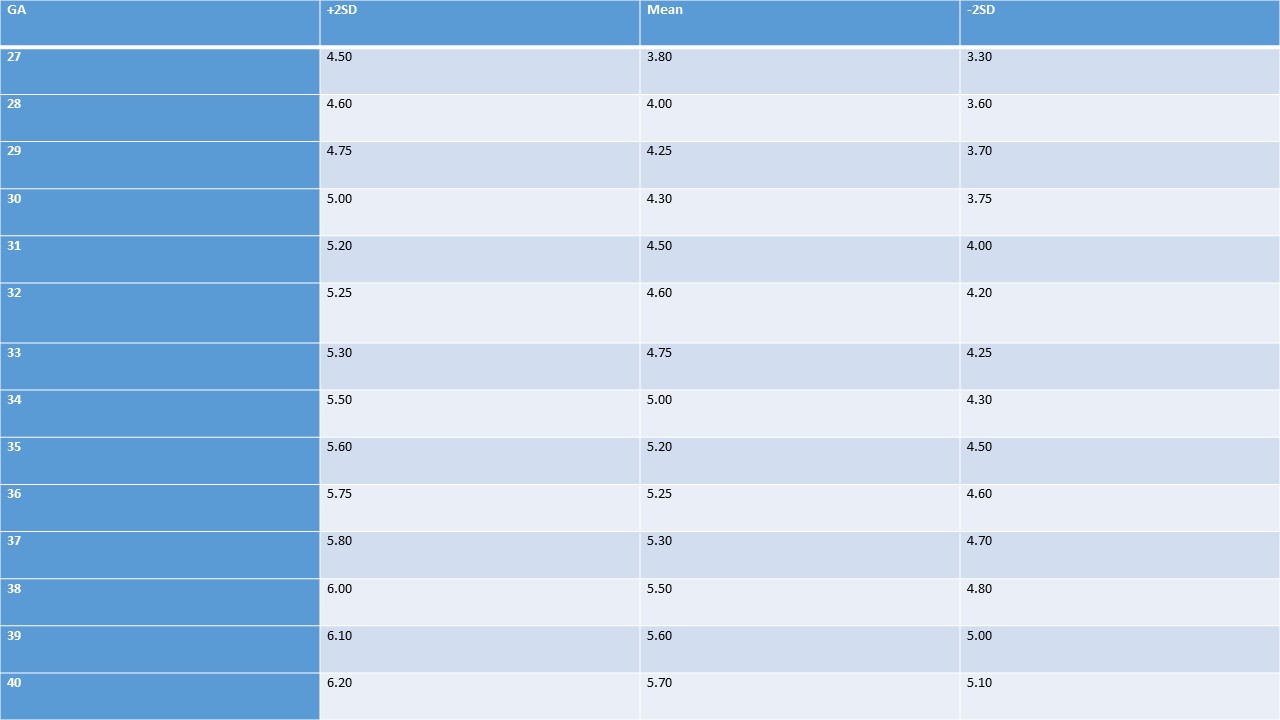
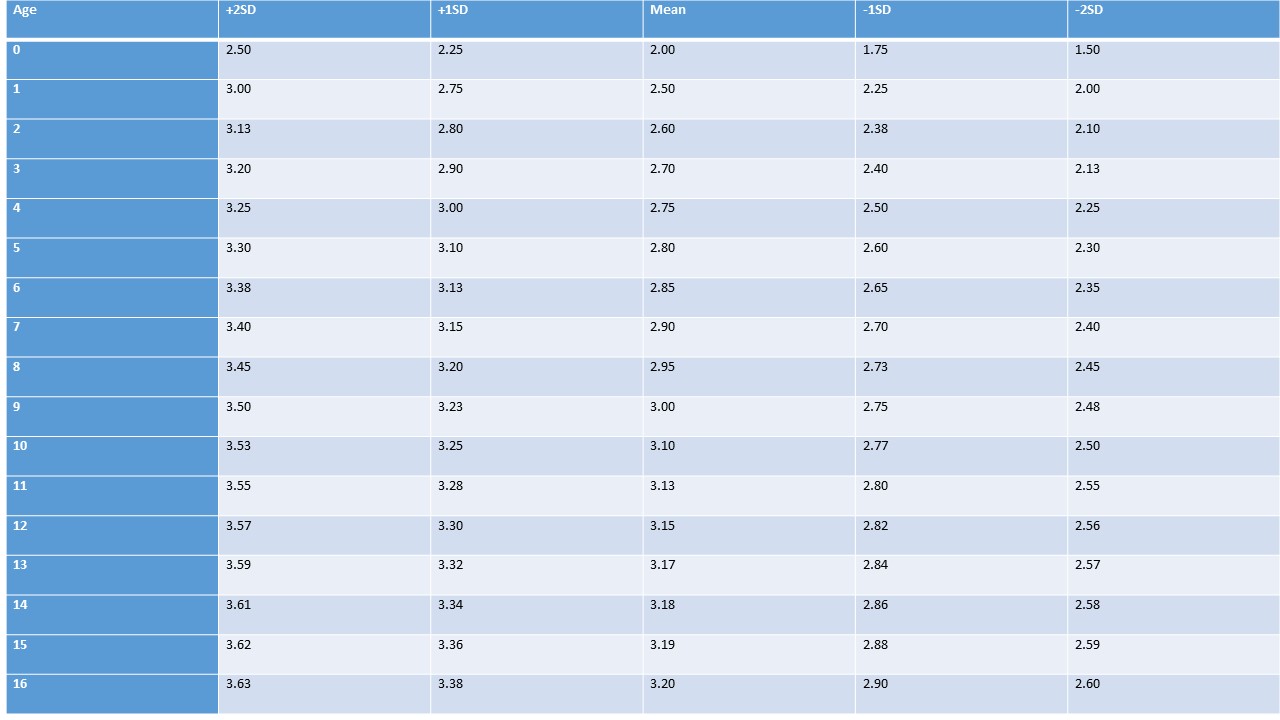
Outer Canthal Distance
Table 1. Outer canthal distance (cm), both sexes, at birth (gestational age in weeks).
Table 2. Outer canthal distance (cm), both sexes, birth to 14 (years).
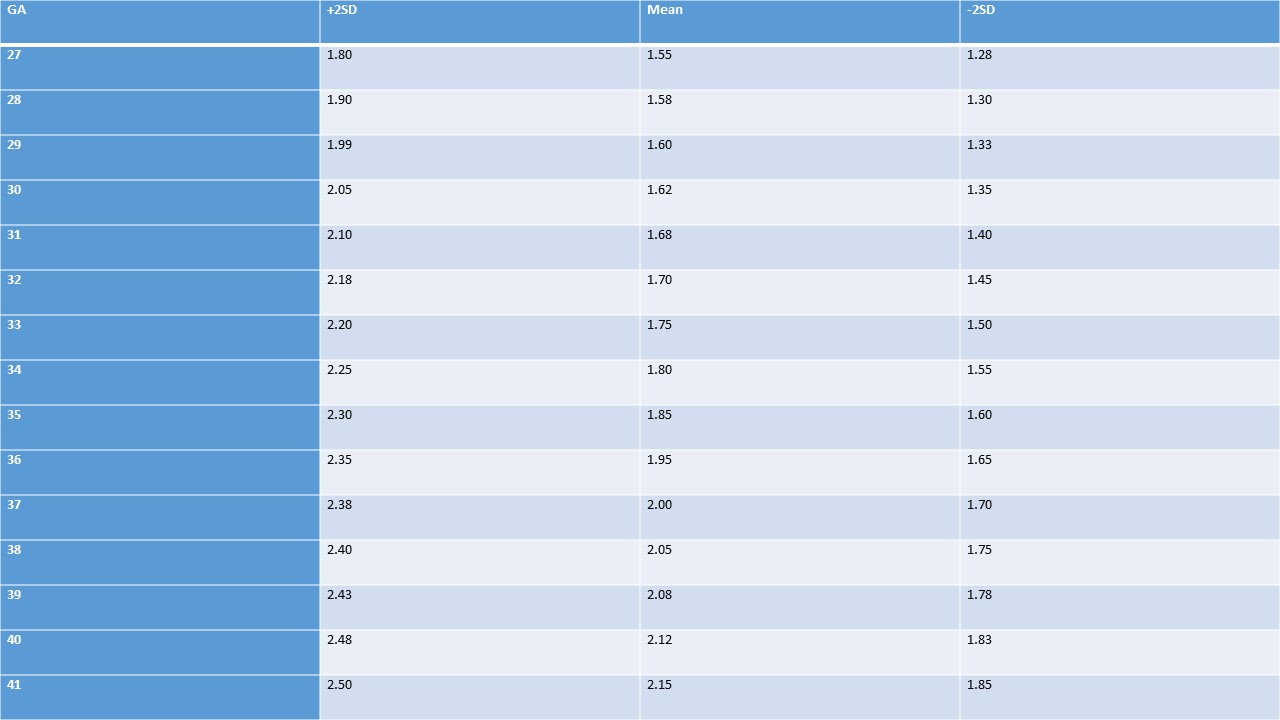
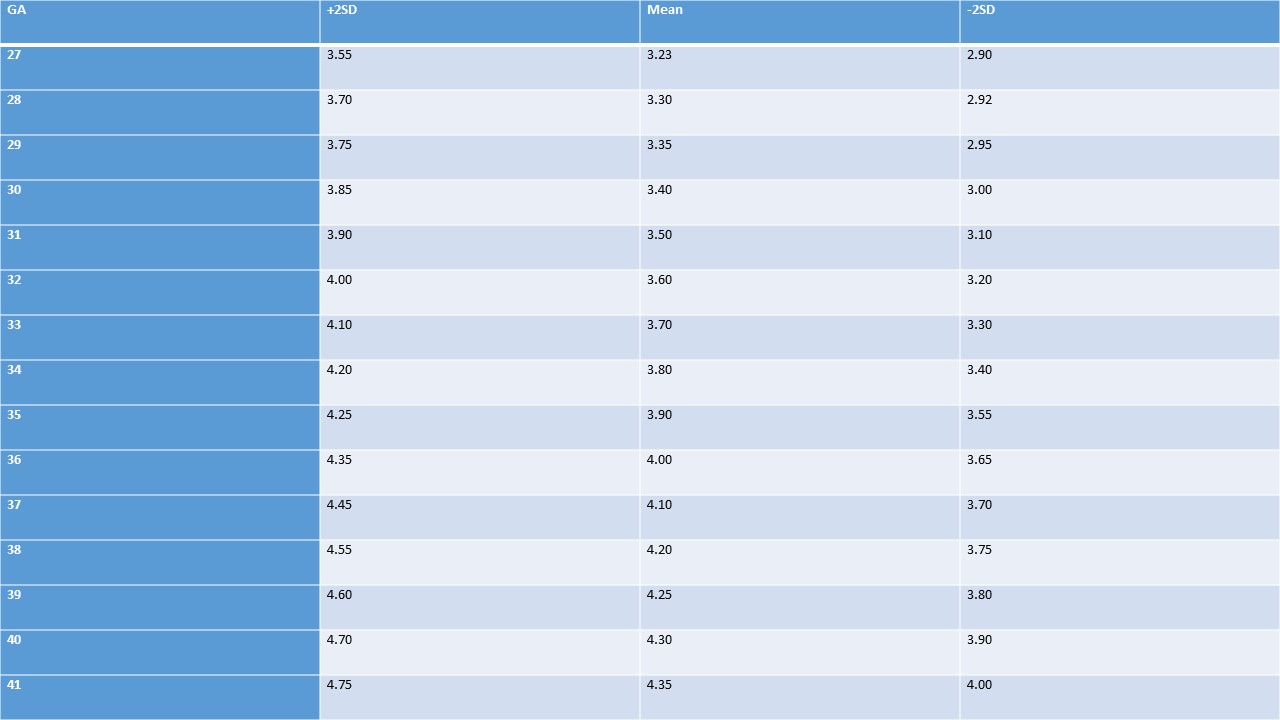
Inner Canthal Distance
Table 3. Inner canthal distance (cm), both sexes, at birth (gestational age in weeks).
--
Table 4. Inner canthal distance (cm), both sexes, birth to 16 (years).
--
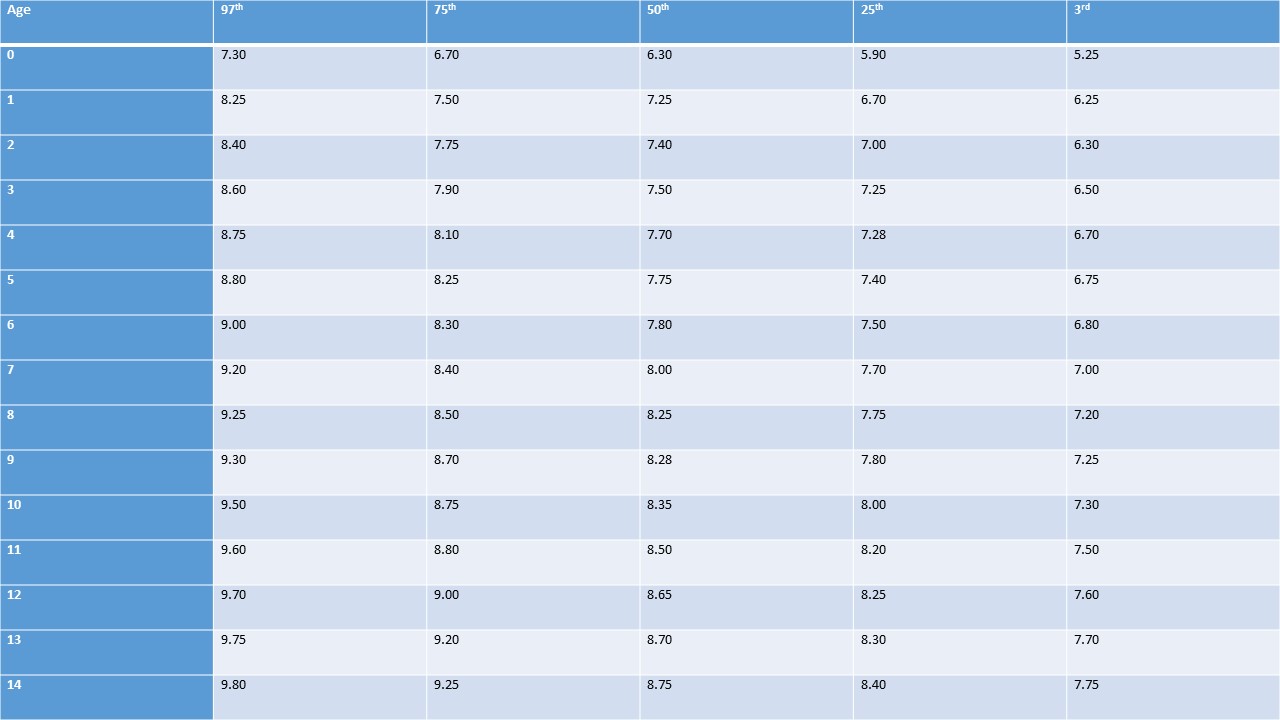
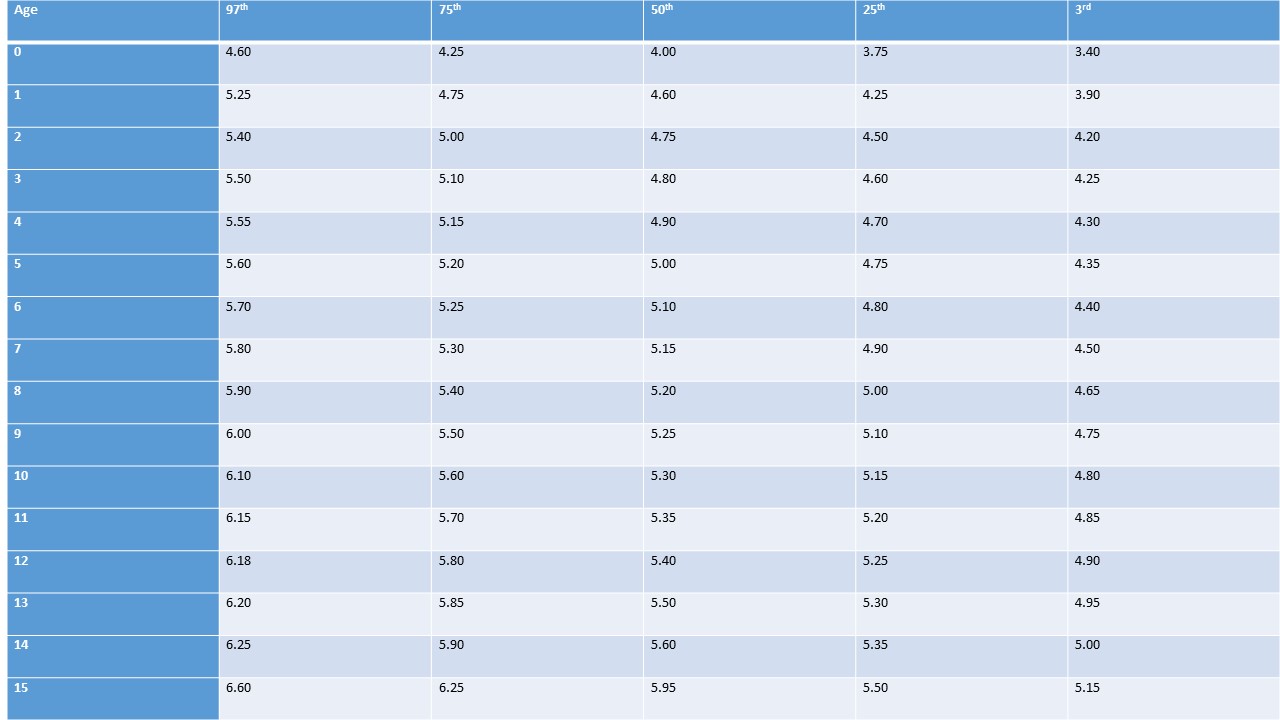
Interpupillary Distance
Table 5. Interpupillary distance (cm), both sexes, at birth (gestational age in weeks).
Table 6. Interpupillary distance (cm), birth to 15 (years).
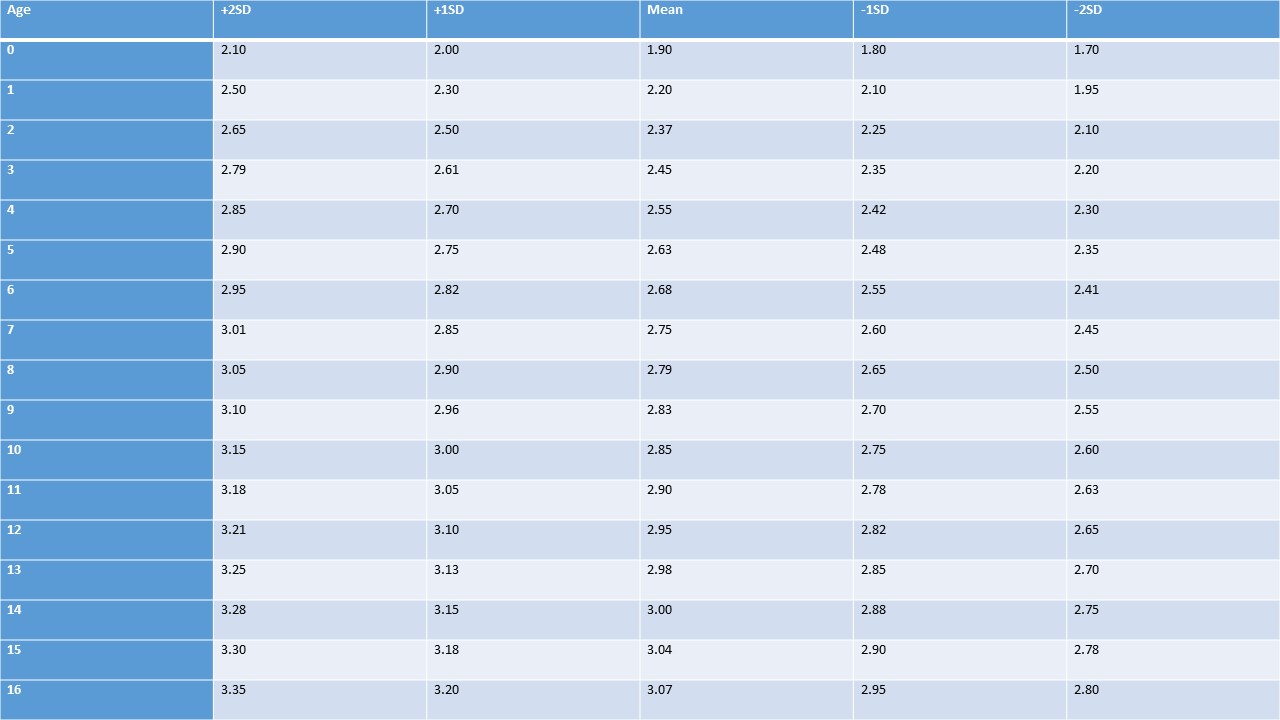
Palpebral Fissure Length
Table 7. Palpebral fissure length (cm), both sexes, birth to 16 (years).
Clinical Features and Associated Conditions
Blepharoptosis (Ptosis)
Definition: Drooping of the upper eyelid.
Figure 2. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting bilateral drooping of the eyelids. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Associated Conditions:
- ARIMA SYNDROME
- BLEPHAROPHIMOSIS, PTOSIS, and EPICANTHUS INVERSUS (BPES)
- CHARGE SYNDROME
- CONGENTIAL FIBROSIS OF EXTRAOCULAR MUSCLES
- CORNELIA DE LANGE SYNDROME
- HORNER’S SYNDROME
- JOUBERT SYNDROME
- JUBERG-MARSIDI SYNDROME
- LEVATOR DEHISCENCE
- KEARNS-SAYRE SYNDROME
- MARCUS GUNN PHENOMENON
- MITOCHONDRIAL ENCEPHALOMYOPATHY, LACTIC ACIDOSIS AND STROKE-LIKE EPISODES (MERRF)
- MITOCHONDRIAL NEUROGASTROINTESTINAL ENCEPHALOPATHY (MNGIE)
- MOYAMOYA DISEASE, SYNDROMIC
- MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE II (HUNTER SYNDROME)
- MUENKE SYNDROME
- MYASTHENIA GRAVIS
- MYOTONIC DYSTROPHY
- NAIL-PATELLA SYNDROME
- NEUROFIBROMATOSIS-NOONAN SYNDROME
- NOONAN SYNDROME
- PETERS-PLUS SYNDROME (KRAUSE-KIVLIN SYNDROME)
- PRIETO SYNDROME
- RUBINSTEIN-TAYBI SYNDROME
- SAETHRE-CHOTZEN SYNDROME
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 1 (LENZ MICROPHTHALMIA SYNDROME)
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 2 (OCULOFACIOCARDIODENTAL SYNDROME
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 13
- THIRD CRANIAL NERVE PALSY
- TRAUMA
- WIEACKER-WOLFF SYNDROME
- WOLFRAM SYNDROME
Downslanting Palpebral Fissures
Definition: Downward slanting of the space between the eyelids
Figure 3. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting downslanting palpebral fissures; image superimposed over reference position. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Associated Conditions:
- APERT SYNDROME
- BEARE-STEVENSON SYNDROME
- BECKWITH-WIEDEMANN SYNDROME
- CHARGE SYNDROME
- CORPUS CALLOSUM, AGENESIS OF, WITH MENTAL RETARDATION, OCULAR COLOBOMA, AND MICROGNATHIA
- CUTIS LAXA, DEBRE TYPE
- MUENKE SYNDROME
- NEUROFIBROMATOSIS-NOONAN SYNDROME
- NOONAN SYNDROME
- ORAL-FACIAL-DIGITAL SYNDROME
- PFEIFFER SYNDROME
- ROIFMAN SYNDROME
- SIMPSON-GOLABI-BEHMEL SYNDROME
- TREACHER COLLINS SYNDROME
Upslanting Palpebral Fissures
Definition: Upward slanting of the space between the eyelids
Figure 4. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting upslanting palpebral fissures; image superimposed over reference position. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Associated Conditions:
- ALAGILLE SYNDROME
- CK SYNDROME
- DOWN SYNDROME
- JUBERG-MARSIDI SYNDROME
- PETERS-PLUS SYNDROME (KRAUSE-KIVLIN SYNDROME)
- PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME
- RENPENNING SYNDROME (MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, RENPENNING TYPE)
- WIEACKER-WOLFF SYNDROME
Anophthalmia
Definition: Absence of one or both eyes
Figure 5. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting right-sided anophthalmia. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Associated Conditions:
- CEREBROOCULONASAL SYNDROME
- CHARGE SYNDROME
- GOLDENHAR SYNDROME (HEMIFACIAL MICROSOMIA)
- GOLTZ SYNDROME
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 1 (LENZ MICROPHTHALMIA SYNDROME)
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 3 (MICROPHTHALMIA AND ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA SYNDROME)
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 4
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 5
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 6
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 9 (MATTHEW-WOOD SYNDROME)
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 12
Microphthalmia
Definition: One or both eyes are abnormally small
Figure 6. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting a microphthalmic right eye; image superimposed over reference position. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Associated Conditions:
- AICARDI SYNDROME
- BLEPHAROPHIMOSIS, PTOSIS, and EPICANTHUS INVERSUS (BPES)
- CEREBROOCULOFACIOSKELETAL SYNDROME
- CHARGE SYNDROME
- CHONDRODYSPLASIA WITH PLATYSPONDYLY, DISTINCTIVE BRACHYDACTYLY, HYDROCEPHALY, AND MICROPHTHALMIA
- DUANE-RADIAL RAY SYNDROME
- GOLDENHAR SYNDROME (HEMIFACIAL MICROSOMIA)
- GOLTZ SYNDROME
- LOWE SYNDROME
- MECKEL SYNDROME
- MUSCULAR DYSTROPHY-DYSTROGLYCANOPATHY
- NANCE-HORAN SYNDROME
- NORRIE DISEASE
- RENPENNING SYNDROME (MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, RENPENNING TYPE)
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 1 (LENZ MICROPHTHALMIA SYNDROME)
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 2 (OCULOFACIOCARDIODENTAL SYNDROME)
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 3 (MICROPHTHALMIA AND ESOPHAGEAL ATRESIA SYNDROME)
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 5
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 6
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 7 (MIDAS SYNDROME)
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 8
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 9 (MATTHEW-WOOD SYNDROME)
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 10
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 11
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 12
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 13
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 14
- WITTWER SYNDROME
Hypertelorism
Definition: Abnormally large distance between the eyes with a wide separation between the medial orbital walls
Figure 7. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting hypertelorism; image superimposed over reference position. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Associated Conditions:
- BARAITSER-WINTER SYNDROME
- DONNAI-BARROW SYNDROME
- HAMAMY SYNDROME
- MECKEL SYNDROME
- OPITZ SYNDROME
- TURNER SYNDROME
Hypotelorism
Definition: Abnormally decreased distance between the eyes
Figure 8. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting hypotelorism; image superimposed over reference position. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Associated Conditions:
- HEREDITARY NEURALGIC AMYOTROPHY
- HOLOPROSENCEPHALY
- MECKEL SYNDROME
- MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA AND DISTINCTIVE FACIAL APPEARANCE
- SCHILBACK-ROTT SYNDROME
Telecanthus
Definition: Abnormally increased distance between the medial canthi of the eyelids with normally positioned medial orbital walls and interpupillary distance
Figure 9. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting telecanthus; Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Associated Conditions:
- AXENFELD-RIEGER SYNDROME
- BLEPHAROPHIMOSIS, PTOSIS, and EPICANTHUS INVERSUS (BPES)
- CORNELIA DE LANGE SYNDROME
- OPITZ SYNDROME
- ORAL-FACIAL-DIGITAL SYNDROME
Proptosis
Definition: Protrusion of the eyeball
Figure 10. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting bilateral proptosis; image superimposed over reference position. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Associated Conditions:
- APERT SYNDROME
- BEARE-STEVENSON SYNDROME
- CROUZON SYNDROME
- CROUZON SYNDROME WITH ACANTHOSIS NIGRICANS (CROUZONODERMOSKELETAL SYNDROME)
- PFEIFFER SYNDROME
- RETINOBLASTOMA
- THYROID OPHTHALMOPATHY
Strabismus
Definition: Eyes that are misaligned. There are various types of strabismus, including esotropia and exotropia, which refers to an inward turning misalignment of the eyes and an outward turning misalignment, respectively.
Figure 11. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting esotropia; image superimposed over reference position. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Figure 12. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting exotropia; image superimposed over reference position. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Associated Conditions (Strabismus):
- ALAGILLE SYNDROME
- ANGELMAN SYNDROME
- ARMFIELD X-LINKED MENTAL RETARDATION SYNDROME
- AXENFELD-RIEGER SYNDROME
- BARDET BIEDL SYNDROME
- BASAL CELL NEVUS SYNDROME
- BLEPHAROPHIMOSIS, PTOSIS, and EPICANTHUS INVERSUS (BPES)
- CHEDIAK-HIGASHI SYNDROME
- CK SYNDROME
- COCKAYNE SYNDROME
- CONGENITAL NYSTAGMUS
- CROUZON SYNDROME
- CROUZON SYNDROME WITH ACANTHOSIS NIGRICANS (CROUZONODERMOSKELETAL SYNDROME)
- CUTIS LAXA, DEBRE TYPE
- DUANE-RADIAL RAY SYNDROME
- DYSKERATOSIS CONGENITA
- GAUCHER’S DISEASE
- GOLDENHAR SYNDROME (HEMIFACIAL MICROSOMIA)
- GOLTZ SYNDROME
- INCONTINENTIA PIGMENTI (BLOCH-SULZBERGER SYNDROME)
- MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA AND DISTINCTIVE FACIAL APPEARANCE
- MICPCH SYNDROME
- OCULAR ALBINISM
- OCULOCUTANEOUS ALBINISM
- ORAL-FACIAL-DIGITAL SYNDROME
- PFEIFFER SYNDROME
- PHACE ASSOCIATION
- PRADER-WILLI SYNDROME
- PRIETO SYNDROME
- PROUD SYNDROME
- RENPENNING SYNDROME (MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, RENPENNING TYPE)
- RETINOBLASTOMA
- ROIFMAN SYNDROME
- RUBINSTEIN-TAYBI SYNDROME
- SAETHRE-CHOTZEN SYNDROME
- SENGERS SYNDROME
- SMITH-MAGENIS SYNDROME (CHROMOSOME 17p11.2 DELETION SYNDROME)
- SPINOCEREBELLAR ATAXIA, X-LINKED 1
- SYNDROMIC MICROPHTHALMIA 2 (OCULOFACIOCARDIODENTAL SYNDROME)
Epicanthal Folds
Definition: A skin fold of the upper eyelid covering the inner corner of the eye
Figure 13. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting epicanthal folds; image superimposed over reference position. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Associated Conditions:
- BECKWITH-WIEDEMANN SYNDROME
- CANTU SYNDROME
- CEREBROOCULONASAL SYNDROME
- CK SYNDROME
- DOWN SYNDROME
- DUANE-RADIAL RAY SYNDROME
- EHLERS-DANLOS SYNDROME
- JOUBERT SYNDROME
- JUBERG-MARSIDI SYNDROME
- MANNOSIDOSIS
- MICPCH SYNDROME
- NEUROFIBROMATOSIS-NOONAN SYNDROME
- NOONAN SYNDROME
- PRIETO SYNDROME
- RUBINSTEIN-TAYBI SYNDROME
- SIMPSON-GOLABI-BEHMEL SYNDROME
Synophrys
Definition: Presence of abundant hair between the eyebrows
Figure 14. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting synophrys. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Associated Conditions:
- BECKWITH-WIEDEMANN SYNDROME
- CORNELIA DE LANGE SYNDROME
- MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE IIIA (SANFILIPPO SYNDROME A)
- MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE IIIB (SANFILIPPO SYNDROME B)
- MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE IIIC (SANFILIPPO SYNDROME C)
- MUCOPOLYSACCHARIDOSIS TYPE IIID (SANFILIPPO SYNDROME D)
- PROUD SYNDROME
- WAARDENBURG SYNDROME
Deep-Set Eyes
Definition: Eyes set far back into the skull giving the appearance of a prominent brow bone
Figure 15. Schematic of the face, frontal view, depicting deep-set eyes; image superimposed over reference position. Illustration courtesy of Taurice N. Couser.
Associated Conditions:
- ALAGILLE SYNDROME
- AVELLINO CORNEAL DYSTROPHY (COMBINED GRANULAR-LATTICE CORNEAL DYSTROPHY)
- BECKWITH-WIEDEMANN SYNDROME
- CEREBROOCULOFACIOSKELETAL SYNDROME
- CHRISTIANSON SYNDROME
- MENTAL RETARDATION, X-LINKED, WITH CEREBELLAR HYPOPLASIA AND DISTINCTIVE FACIAL APPEARANCE
- MOYAMOYA DISEASE, SYNDROMIC
References
- ↑ Feingold M., Bossert WH, Normal values for selected physical parameters: An aid to syndrome delineation. Birth Defects 10:1-16, 1974.
- ↑ Hall JG, Froster-Iskenius UG, Allanson JE, Handbook of Normal Physical Measurements, Oxford, UK, Oxford University Press, 1989.
- ↑ Sivan Y, Merlob P, Reisner SH, Eye Measurements in preterm and term newborn infants., J Craniofac Genet Dev Biol, 1982;2(3):239-42.
- ↑ Thomas IT, Gaitantzis YA, Frias JL, Palpebral fissure length from 29 weeks gestation to 14 years., J Pediatr, 1987 Aug;111(2):267-8.
- ↑ Hall BD, Graham JM Jr., Cassidy SB, Opitz JM., Elements of Morphology: Standard Terminology for the Periorbital Region, Am J Med Genet Part A 149A:29-39, 2009.
- ↑ Laestadius, N. D., Aase, J. M., Smith, D. W. Normal inner canthal and outer orbital dimensions. J. Pediat. 74: 465-468, 1969.
- ↑ Fundamentals and Principles of Ophthalmology, Section 2 Basic and Clinical Science Course, American Academy of Ophthalmology, 2006.
- ↑ Kate Ahmad, Mark Wright, Christian J Lueck, Ptosis, Pract Neurol. 2011;11(6):332-340.
- ↑ Greig DM. Hypertelorism: A hitherto undifferentiated congenital craniofacial deformity. Edinb Med J. 1924;31:460.
- ↑ Cohen MM Jr. Craniofrontonasal dysplasia. Birth Defects Orig Artic Ser. 1979;15(5B):85-9.
- ↑ Michael Mercandetti, Exophthalmos, Medscape Reference. Updated May 30, 2014.
- ↑ Online Mendelian Inheritance in Man, OMIM®. McKusick-Nathans Institute of Genetic Medicine, Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, MD), World Wide Web URL: http://omim.org/