Intratunnel Phacofracture: A New MSICS Technique
All content on Eyewiki is protected by copyright law and the Terms of Service. This content may not be reproduced, copied, or put into any artificial intelligence program, including large language and generative AI models, without permission from the Academy.
In 2012, Dr, Sudhir Singh,MS published a new manual small-incision cataract surgery (MSICS) technique based on his experience at Global Hospital Research Centre, Mount Abu, India [1][2].The MSICS and phacoemulsification are the most popular methods of cataract extraction today. The former is significantly faster, less expensive, and less technology-dependent than phacoemulsification and has been extensively practiced in developing countries such as India. However, the draw-back of most commonly practiced MSICS techniques— Blumenthal, visco expression, irrigating wire vectis, and fish-hook needle—is that they all require a large incision of 7 to 9 mm, which leads to induced astigmatism. In the intratunnel phacofracture technique, the lens nucleus is broken inside a sub−6-mm sclerocorneal tunnel incision and removed. The nucleus removal steps take place inside the sclerocorneal tunnel, in contrast with other nucleotomy techniques in which this maneuvering takes place inside the anterior chamber.
Intratunnel Phacofracture Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery Basics
Watch Video of Intratunnel Phacofracture on YouTube https://youtu.be/_nYIR3n_--o?list=PLO6iZMCr0FmxCYmg7Pxq_lf07K9Ki8CTA
Topical Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery HD (Unedited)
Intratunnel Phacofracture MSICS In White Cataract Surgery Video on YouTube
Why All Cataract Surgeons Should Learn Manual SICS Too on YouTube
Anesthesia
Manual small incision cataract surgery can be performed under peribulbar or topical anesthesia.
Site of Incision
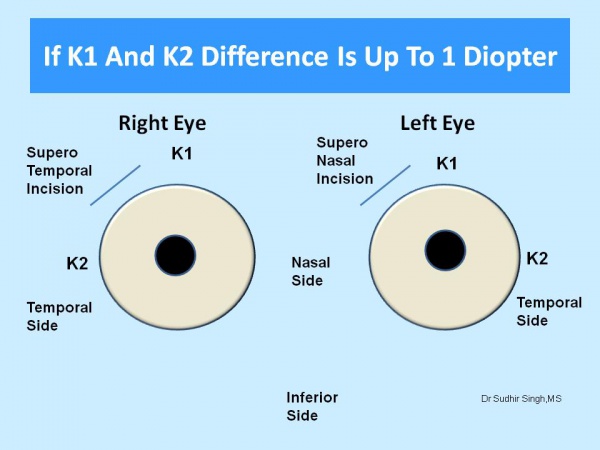
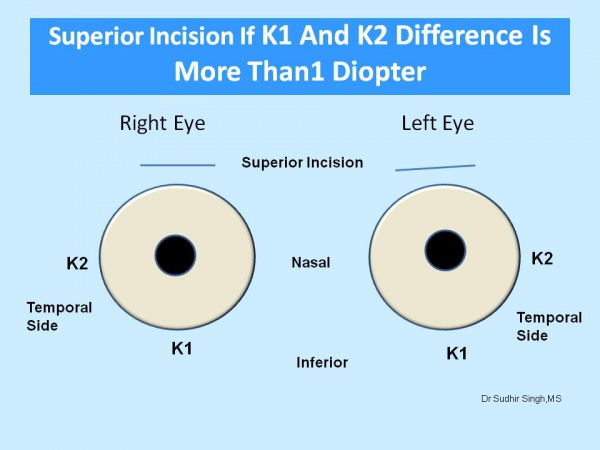
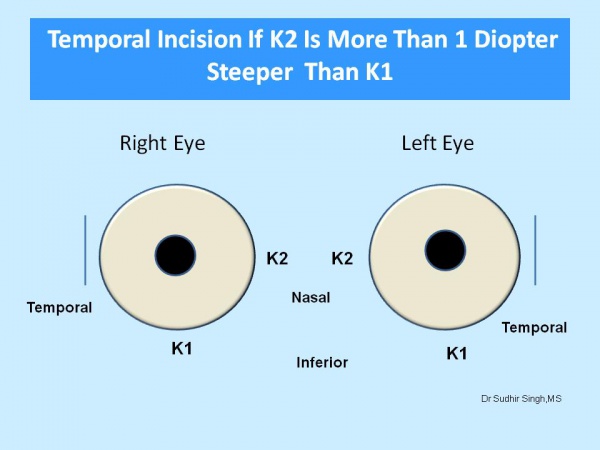
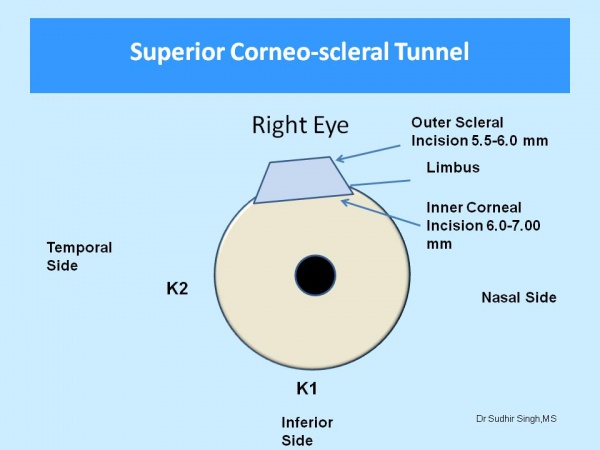
The site of the incision is chosen according to keratometry values (K1 and K2). The supratemporal quadrant for the right eye and the superonasal quadrant for the left eye should be chosen if the difference between K1 and K2 is equal or less than 1.0 diopter (Figure 1). If the difference between the K1 and K2 is more than 1.0 diopter then the incision should be on the steeper axis. If K1 is steeper than K2 then superior incision (Figure 2) and If K2 is steeper than K1 then temporal incision (Figure 3).
Figure 1: If the difference between K1 and K2 is less than 1 diopter then superotemporal incision for the right eye and superonasal for the left eye.
Figure 2: If K1 is more than 1.0 diopter from K2 then superior incision for both eyes.
Figure 3: If K2 is more than 1.0 diopter from K1 then temporal incision for both eyes.
Surgical Steps
Cleaning and draping
The skin of the eyelids, lid margins and around the eye is cleaned with 10 percent solution of povidone-iodine solution. Drape is applied. Wire speculum is placed. The cul de sac is thoroughly washed with Ringer’s lactate or balanced salt solution.
Superior Rectus Bridle Suture
A 4/0 silk superior rectus bridle suture is placed beneath the tendon of the superior rectus muscle. It is helpful to position the eye after local anesthesia. Superior rectus bridle suture is not used when surgery is planned under topical anesthesia.
Conjunctival Flap
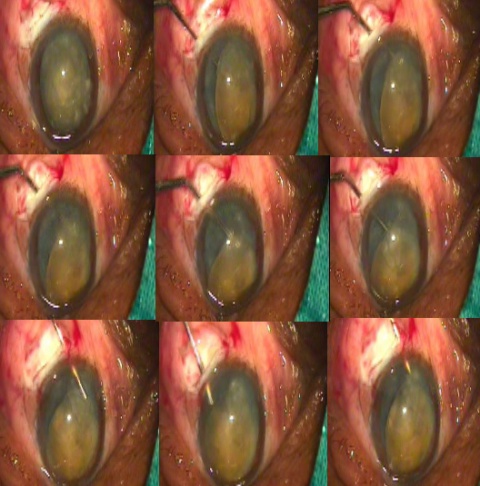
A fornix-based conjunctival flap at the limbus with a chord length of approximately 6.5 mm is made. After careful dissection of Tenon’s capsule, light cautery is applied (Figure 4).
Figure 4: Fornix-based conjunctival flap, cautery and partial scleral groove demonstration
Video : Fornix Based Conjunctival Flap Making
Video : Cautary
Sclera-corneal Tunnel
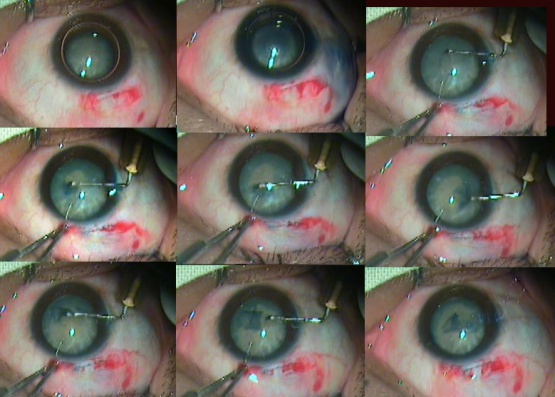
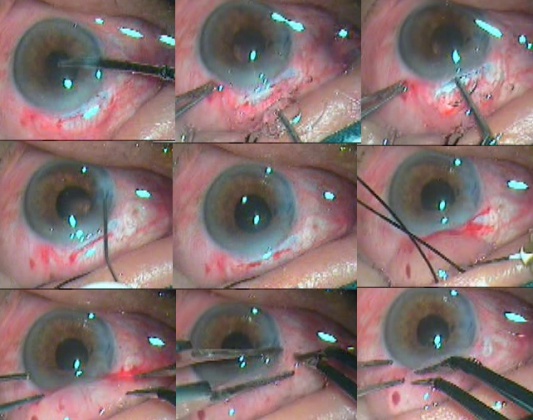
A 4- 6 mm scleral frown incision, 1.5 mm from the limbus is made with a 15-number Bard Parker blade (Figure 5). A funnel-shaped sclerocorneal tunnel incision is created with a steel crescent knife. One side port is made 90 degrees apart on either side of the scleral tunnel with a 15-degree knife temporally in the right eye and nasally in the left eye. With a 2.8 mm keratome, the anterior chamber is entered 1.5 mm into the clear cornea. The anterior chamber is entered with 1.5 mm in the clear cornea with help of 3.2 mm keratome (Figure 6). The hydroxyl propyl methyl cellulose 2 % (HPMC) viscoelastic is injected into the anterior chamber.
Figure 5: Sclerocorneal tunnel-making demonstration
Figure 6: Illustrates sclerocorneal tunnel dimensions in superior quadrant
Sclerocorneal Tunnel Construction Video
Central Circular Capsulorhexis
Then viscoelastic is injected and the capsulorhexis is made. The central circular capsulorhexis is made with the help of a 26-gauge needle capsulotome. If the glow is poor then the capsule was stained with trypan blue dye under an air bubble. The size of capsulorhexis is depends on the size of the nucleus. It may vary from 5.5 mm to 7.5 mm (Figure 7). If the nucleus size is anticipated large then two relaxing incisions are made at the margins of the capsulorhexis. Capsulorhexis can also be made by capsulorhexis forceps.
Figure 7: Capsular staining and capsulorhexis creation with 26 G needle capsulotome
Capsular Staining Video
Capsulorhexis Animation Video on YouTube
Capsulorhexis In Different Situations
Hydrodissection Procedure
The hydro dissection is made with 26-gauge cannula placed on 2 CC syringe filled irrigating fluid.
Hydro dissection Video
Nucleus Prolapse in the Anterior Chamber
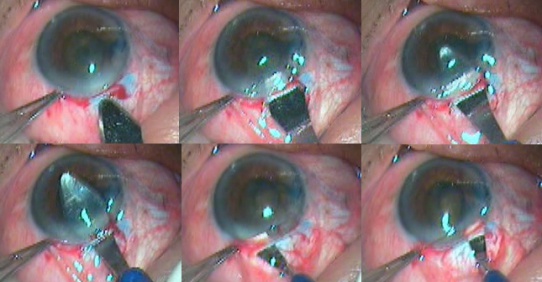
The internal incision of the tunnel is enlarged sideways to 7 mm with a 5.1 mm keratome (Figure 8) . The anterior chamber is formed again with viscoelastic and the nucleus is rotated within the capsule using a Sinskey hook. The nucleus prolapsed into the anterior chamber using a Sinsky hook. A Sinskey hook is used to retract the capsulorhexis to engage the equator, lever out one pole of the nucleus outside the capsular bag, and the rest of the nucleus is rotated into the anterior chamber. If the nucleus is too large then two or three relaxing incisions are made at the capsulorhexis margins at equidistant (Figure 9).
Figure 8: Tunnel enlargement with 5 mm keratotome and enlargement of the internal incision with 2.8 mm keratotome
Figure 9: Demonstration of the nucleus rotation and prolapse in anterior chamber
Nucleus Prolapse Into The Anterior Chamber Video
Nucleus Management
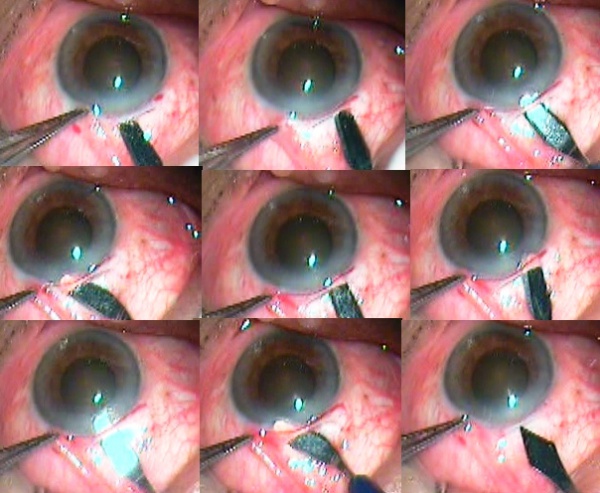
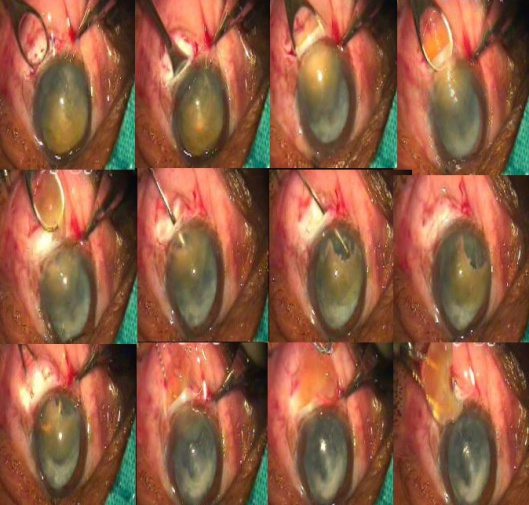
Up to this step, all the above-mentioned steps are the same as in other manual small incision techniques. Intratunnel phacofracture technique now diverges from other phacofracture techniques. Enough viscoelastic is placed between the cornea and the superior surface of the nucleus to protect the endothelium as well as between the nucleus and iris. The nucleus is taken out from the capsule using a Sinskey hook. The globe is stabilized with tooth forceps and the small Lewis lens loop is introduced through the tunnel and positioned between the iris and the nucleus. The nucleus is engaged in the lens loop and slowly withdrawn from the anterior chamber while the posterior lip of the tunnel is depressed. Once the nucleus gets engaged in the tunnel, then the Lewis loop is pulled posteriorly and upwards. This causes the breaking and removal of a part of the nucleus and the other part remains engaged in the tunnel. Using the viscoelastic cannula, the engaged part of the nucleus is pushed back into the anterior chamber and rotated so its longitudinal axis coincides with the tunnel axis. Again, viscoelastic is placed between the cornea and the superior surface of the nucleus and between the nucleus and the iris. The lens loop is introduced through the tunnel and positioned between the iris and the remaining part of the nucleus. The remaining part of the nucleus is engaged in the lens loop and slowly withdrawn from the anterior chamber while the posterior lip of the tunnel is depressed. Most of the time the remaining part of the nucleus comes out. If it still breaks down then the remaining part is again pushed in the anterior chamber with help of viscoelastic and previous steps are repeated till it comes out (Figure 10).
Figure 10: Demonstration of intratunnel phacofracture using Levis lens loop
Intratunnel Phacofracture MSICS Mechanism Animation
Cortical Matter Clean Up
The remaining cortical matter cleanup is done with direct 23-gauge Simcoe irrigating aspirating cannula. The anterior chamber is formed with Viscoelsatics (Figure 11).
Safe Irrigation Aspiration Animation Video on YouTube
Intraocular Lens Implantation
A single-piece PMMA intraocular lens of 5.5-6.00 mm optic size and 12.5 mm total size is implanted into the capsular bag. The anterior chamber is washed out thoroughly by Simcoe irrigation aspiration canula using Ringer’s lactate solution (Figure 11).
Figure 11: Irrigation aspiration, intraocular lens implantation, wound sealing and conjunctival flap re positioning
Anterior Chamber Wash
Conjunctival Flap Reposition
The conjunctival flap is reposited back and cauterized at the edges.
Conjunctival Flap Reposition Video
Main Ports and Side ports Sealing
The main port and side ports are sealed with stromal hydration using a 26-gauze cannula. A 0.5 cc sub-conjunctival gentamycin with dexamethasone injection is given. The eye is pad patched
Intratunnel Phacofracture Manual Small Incision Videos in Different Types of the Cataracts
Combined Intratunnel Phacofracture MSICS and Trabeculectomy Unedited HD
Intratunnel Phacofracture MSICS in Intumescent White Cataract
Intratunnel Phacofracture MSICS In Cataract with Pseudo Exfoliation and Non-Well Dilated HD
Intratunnel Phacofracture MSICS in Hard Nuclear Cataract Grade 4
6 mm Intratunnel Phacofracture MSICS Hyper Mature White Cataract HD (Unedited)
6 mm Intratunnel Phacofracture MSICS With Astigmatism Controlling Sutures HD (Unedited)
Intratunnel Phacofracture MSICS in White Cataract with Phacodonesis Unedited HD
Intratunnel Phacofracture SICS In Nuclear Cataract Grade 4 With Non-Well Dilated Pupil (Unedited) HD
4 mm Intratunnel Phacofracture MSICS in White Cataract with Foldable IOL
Management of Subluxated Cataract by SICS With CTR and IOL
References
- ↑ Sudhir Singh. First Postoperative Day Visual Outcome Following 6 mm Manual Small Incision Cataract Surgery Using Intratunnel Phacofracture Technique. US Ophthalmic Review, 2014;7(1):26–30 .[1]
- ↑ Sudhir Singh.Step By Step:intratunnel Phacofracture.Cataract & Refractive Surgery Today Europe.May 2016:38-41. [2]