Ocular Trauma Score
All content on Eyewiki is protected by copyright law and the Terms of Service. This content may not be reproduced, copied, or put into any artificial intelligence program, including large language and generative AI models, without permission from the Academy.
Ocular Trauma Score
The Ocular Trauma Score (OTS) was proposed by Kuhn et al in the early 2000s to provide a simple system with few variable to predict final visual outcome of an injured eye. Approximately 2,500 patients were evaluated and over 100 variables were selected from to build the OTS.
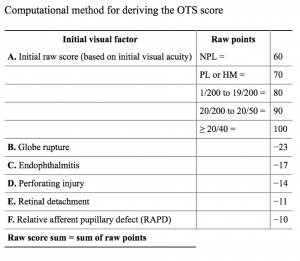
The variables used in the OTS are the initial visual acuity and then presence (or absence) of the following: globe rupture, endophthalmitis, perforating injury, retinal detachment (RD) and afferent pupillary defect (APD).
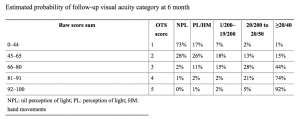
To calculate the raw score, add A+ B+C+D+ E+F (see chart). Conversion of the raw score into the OTS can predict likelihood of final vision into categories per the chart to the bottom right.
A variation of the OTS, the pediatric OTS (POTS), has been studied and may be more useful in the pediatric population.
Significance of the OTS
For patients, knowing their OTS can help set their expectations for long term outcomes. This can provide reassurance if they have a good prognosis and help them to make tough decisions (e.g. whether to go forward with elective enucleation).
For the ophthalmologist, the OTS can help when they are counseling a patient and when deciding how to best proceed surgically. Additionally, the OTS can be used for research purposes when evaluating outcomes after ocular injuries.
References
1. Kuhn F, Maisiak R, Mann L, Mester V, Morris R, Witherspoon C (2002) The Ocular Trauma Score (OTS). Ophthalmol Clin North Am 15: 163−166
2. Kuhn F, Maisiak R, Mann L, Morris R, Witherspoon C (2002) The Ocular Trauma Score (OTS): Prognosticating the final vision of the seriously injured eye. In: Kuhn F, Pieramici D (eds) Ocular trauma: principles and practice. Thieme, New York, pp 14−12
3. Weichel ED1, Colyer MH, Ludlow SE, Bower KS, Eiseman AS. Combat ocular trauma visual outcomes during operations iraqi and enduring freedom. Ophthalmology. 2008 Dec;115(12):2235-45. doi: 10.1016/j.ophtha.2008.08.033.
4. Acar U, Tok OY, Acar DE, Burcu A, Ornek F. A new ocular trauma score in pediatric penetrating eye injries. Eye (Lond). 2011 Mar;25(3):370-4. doi: 10.1038/eye.2010.211.