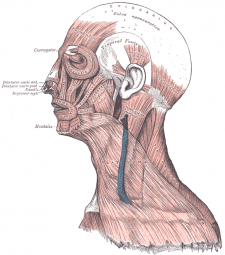
Facial Anatomy - Muscles
All content on Eyewiki is protected by copyright law and the Terms of Service. This content may not be reproduced, copied, or put into any artificial intelligence program, including large language and generative AI models, without permission from the Academy.
The muscles of facial expression are derivatives of the 2nd pharyngeal arch and are innervated by facial nerve (CN VII)[1]. These muscles originate from bone or fascia and insert on skin to provide the movements of facial expression. The muscles of facial expression are enclosed by, or form part of, the superficial musculo-aponeurotic system (SMAS).[2]
Orbital Group
The orbital group consists of the orbicularis oculi (3 portions), depressor supercilii, and corrugator supercilii (oblique and transverse heads). These muscles provide movement of the eyelid, eyebrow, and periorbital skin and are innervated by branches of the facial nerve [1].
|
|---|
Oral Group
The oral group consists of the orbicularis oris, depressor anguli oris, levator anguli oris, zygomaticus major, zygomaticus minor, levator labii superioris, levator labii superioris alaeque nasi, risorius, depressor labii inferioris, mentalis, and buccinator. These muscles provide movement of the lips and are innervated by branches of the facial nerve[1].
|
|---|
Nasal Group
The nasal group consists of the compressor naris and dilator naris of the nasalis, depressor septi, and procerus. These muscles provide movement of the nose and perinasal skin and are innervated by branches of the facial nerve[1].
|
|---|
Auricular Group
The auricular group consists of the anterior, superior, and posterior auricular muscles. These muscles provide movement of the auricle and are innervated by the temporal and posterior auricular branches of the facial nerve[1].
|
|---|
Occipitofrontalis Group
The occipitofrontalis, or scalp, group consists of the frontalis, and occipitalis. These muscles provide movement of the eyebrows, forehead, and scalp and are innervated by the temporal and posterior auricular branches of the facial nerve [1].
|
|---|
Neck Group
The neck group consists of the platysma. It provides movement of the skin of the neck and is innervated by the cervical branch of the facial nerve [1].
|
|---|
Muscles of Mastication
The muscles of mastication are derivatives of the first pharyngeal arch and are innervated by the mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V) [2]. These muscles originate and insert on bone and provide movement of the mandible to enable mastication. The muscles of mastication consist of the temporalis, masseter, medial ptyergoid, and lateral pterygoid [3].
|
|---|
References
- ↑ Jump up to: 1.0 1.1 1.2 1.3 1.4 1.5 1.6 Norton, Neil S. "Scalp and muscles of facial expression." Norton, Neil S. Netter's Head and Neck Anatomy for Dentistry. 2. Saunders, and imprint of Elsevier Inc., 2012. 153-184.
- ↑ Jump up to: 2.0 2.1 Afifi, Ahmed M. and Risal Djohan. "Anatomy of the head and neck." Neligan, Peter C. Plastic Surgery. 3. Elsevier, Inc., 2013. 1, 3-22.e5.
- ↑ "Head and Neck." Drake, Richard, A. Wayne Vogl and Adam W. M. Mitchell. Gray's Anatomy for Students. 3. Churchill Livingstone, an imprint of Elsevier Inc., 2015. 835-1135.