Embryology of the Eye and Ocular Adnexa
All content on Eyewiki is protected by copyright law and the Terms of Service. This content may not be reproduced, copied, or put into any artificial intelligence program, including large language and generative AI models, without permission from the Academy.
The development of the eye is a marvel of complexity, involving a series of intricate and precisely timed cascading cellular events, choreographed by a set of molecular signals and genetic programs. Here we will provide a overview of ocular embryology, covering the key stages and events involved in the development of the eye, as well as the genetic and molecular signals that regulate this process.
As an ophthalmologist, having a solid foundation in ocular embryology can prove critical for recognizing and managing congenital eye disorders. By the end of this article, the reader should have a better understanding of ocular embryology and its relevance to clinical practice.
Early Embryologic Development
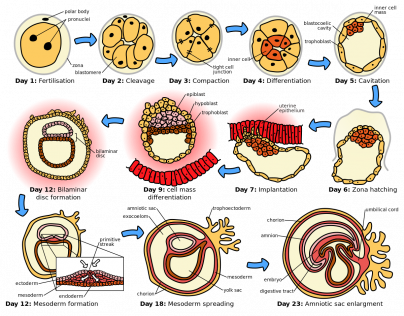
The development of the eye begins with a process called gastrulation. This critical event transforms the blastula (a hallow sphere of cells) into a gastrula (charactized by the formation of three distinct germ layers - the endoderm, mesoderm, and ectoderm). These three germ layers give rise to all the major tissues and organs in the body, including those necessary for ocular development. By the third week of development, the three germ layers are arranged in a flat disc-like structure called the trilaminar disc, which marks a key milestone towards the formation of the developing embryo.
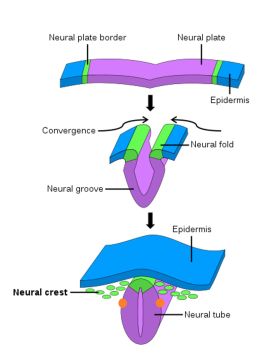
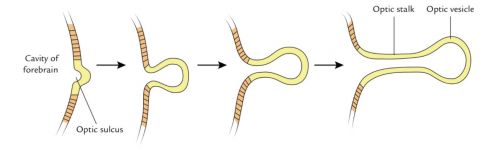
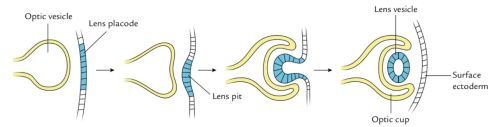
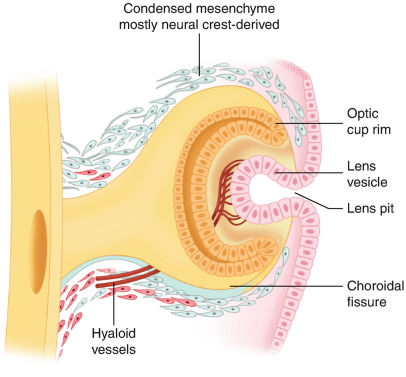
Soon after gastrulation, the embryo then undergoes neurulation (Figure 1). During neurulation, a flat sheet of cells called the neural plate folds in on itself to form the neural tube. Around day 22 of gestation, the optic grooves emerge on the neural folds (Figure 1 - orange dots), evolving into optic vesicles by day 25. These vesicles contact the surface ectoderm, inducing the formation of the lens placode (Figures 2 and 3). The proximal portion of the vesicle (the optic stalk) will ultimately become the optic nerve, where the distal portion invaginates to form the optic cup (and is destined to become the future retina, iris, and ciliary body).
Development of Individual Structures
Eyelids and Conjunctiva
During the fifth week of gestation, the eyelids begin to form from contributions of both neural crest-infiltrated mesenchyme and nearby surface ectoderm. By week seven, two distinct eyelid folds are apparent, and epithelial cells begin to invaginate in the area of the medial lid margins, forming the precursors to the future lacrimal puncta and canaliculi.[1] During week eight, the upper and lower lids proceed to refuse via epithelial cell migration and proliferation.[2] The eyelids remain closed until the 26th to 28th week, protecting the developing cornea and conjunctiva. During this period of fusion, mesenchymal cells infiltrate the lids and form the palpebral musculature.[3]
Lacrimal Gland
The lacrimal gland begins its development in the seventh week of gestation. Each gland is derived from a set of 15-20 neural crest-derived glandular buds at the superolateral angle of the conjunctival sac.[4] Notably, while the lacrimal gland develops acini and the lacrimal ducts canalized while still in-utero, in a significant minority of infants, reflex tear production does not begin until weeks 1-3 of life.[5]
Lens
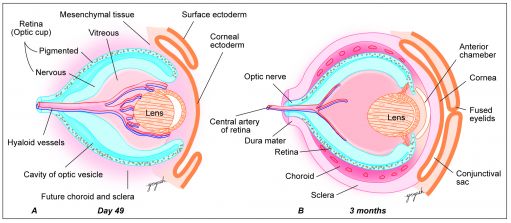
Lens formation begins when the optic vesicle induces inward invagination and budding of the overlying surface ectoderm to form the lens vesicle (Figure 3).[6] The posterior cells of the lens vesicle elongate anteriorly to form primary lens fibers, filling the lumen by the seventh week. Secondary lens fibers continue to develop throughout life, contributing to lens growth. Lens development obtains nutrition via derivatives of the hyaloid artery. Later, after hyaloid artery regression, lens nourishment is supplied via the aqueous humor.
Cornea
The cornea develops from multiple sources: the epithelium arises from surface ectoderm, while the stroma and endothelium originate from neural crest cells. By the eighth week, the cornea is composed of five distinct layers. The corneal epithelium is a derivative of surface ectoderm proximal to the developing lens (Figure 3). The corneal stroma and endothelium are derived from successive waves of invading neural crest cells. [7] The mature, transparent cornea is the result of mesenchymal-derived stromal keratocytes producing a highly organized stromal collagen matrix.
Iris and Ciliary Body
The iris and ciliary body are a product of the anterior rim of the optic cup (Figure 5). The inner and outer layers of the anterior rim, induced by surrounding mesenchymal development, give rise to the posterior and anterior portions of iris epithelium respectively.[8] The intrinsic muscles of the iris (sphincter pupillae and dilator pupillae) are derived from the surrounding neuroectoderm, whereas the ciliary muscle, the structure eventually responsible for changing the shape of the mature lens, is derived from invading neural crest cells.[9] Neural crest cells also produce the stroma of the iris, which, based on its eventual concentration of melanocytes, is the largest determinant of the mature iris color.
Vitreous
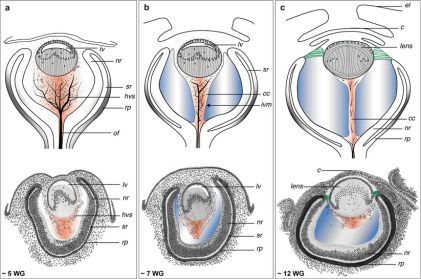
The vitreous is primarily composed of a gel-like substance called vitreous humor, and is a mesenchymal derivative. The developmental progression of the vitreous can be thought of as a succession of three distinct phases. The first phase, termed the primary vitreous function to house the hyaloid vasculature as it provides nourishment to the developing anterior segment (Figure 6). As the primary vitreous and hyaloid vasculature regress, they are succeeded by the acellular, avascular secondary vitreous, which ultimately forms the bulk of what is thought of as the mature vitreous. Regression of the primary vitreous leaves behind Cloquet's canal, a vestigial structure that run through the vitreous body from the optic nerve disc to the lens in the mature eye and is sometimes visible in the mature eye.[10] The final step of vitreous development comes when tertiary vitreous form the lens zonules.[11]
Retina
As previously mentioned, the optic cup rim (anterior 1/5 of the optic cup) is the precursor to the iris and ciliary body. The remaining 4/5ths of the optic cup ultimately gives rise to the retina. This inner 4/5ths, which is termed the optic cup body, is composed of two layers, each with distinct structural destinies. The thinner, outer layer becomes the retinal pigmented epithelium (RPE), while the thicker, inner layer is what forms the neural retina.[6] Of note, the RPE is the only pigmented tissue in the body not derived from neural crest cells (instead being derived from neural ectoderm). By the eighth month, the retina achieves a layered structure that resembles the mature eye.
Choroid and Sclera
The choroid and sclera are formed when mesenchyme proximal to the optic cup condenses into two layers, an inner vascular layer (future choroid), and an outer fibrous layer(future sclera).
Extraocular Muscles
The formation of the extraocular muscles (EOMs) is the result of three distinct developmental epicenters in the embryonic cranium (preotic myotomes). Starting very early in development, each myotome has an associated cranial nerve (CNs III, IV, and VI) and these nerves associations persist into maturing, providing innervation to the respective mature EOM(s).
Orbit
The structures of the bony orbit are primary a product of neural crest linage, along with a few minor contributions from mesoderm and ectoderm.[12] The orbit starts off as a loose network of undifferentiated mesenchymal cells and begin to ossify in the sixth gestational week.[13] The bones of the orbit develop by direct intramembranous ossification, with the exception of the sphenoid and the ethmoid bones which develops via endochondral ossification (characterized by a preceding cartilaginous phase).[14]
| Ocular Structure | Embryologic Origin |
|---|---|
| Eyelids | Surface ectoderm (epithelium, conjunctiva, lacrima/meibomian glands), mesoderm |
| Corneal epithelium | Surface ectoderm |
| Corneal stromal and endothelium | Neural crest |
| Sclera | Neural crest (with minor mesoderm contribution to temporal sclera) |
| Iris epithelium | Neural ectoderm |
| Iris stroma | Mesoderm and neural crest |
| Ciliary body epithelium | Neural ectoderm |
| Ciliary body | Mesoderm |
| Trabecular meshwork | Neural crest |
| Lens | Surface ectoderm |
| Vitreous body | Neuroectoderm (largest contributor by volume) |
| Retina and RPE | Neural ectoderm |
| Choroid | Mesoderm and neural crest |
| Extraocular muscles | Mesoderm |
| Optic nerve | Neural ectoderm |
| Orbital fat | Neural crest and mesoderm |
| Orbital bones | Neural crest (primarily) |
| Gene name | Gene function(s) | |
|---|---|---|
| PAX 6 | "Master" gene in the development of the eye; mutations are associated with coloboma, microphthalmia, and Peter’s anomaly[15] | |
| SHH | Responsible for the division of the eye field into two globes; mutations are associated with cyclopia | |
| PAX 2 | Essential for optic stalk formation and the closure of the retinal fissures[16] | |
| Rx | Essential for optic vesicle evagination and PAX6 expression, may also play a role in retinal differentiation and proliferation[6] | |
| BMP4 | Induces the surface ectoderm that overlies the optic vesicle to form a lens placode | |
| Nrl | Important regulator of rod photoreceptor development |
All images were obtained via a creative common license or direct approval from the original creator.
- ↑ Ali MJ, Kakizaki H. Embryology of the lacrimal drainage system. In: Ali MJ, editor. In: Principles and Practice of Lacrimal Surgery. New Delhi, India: Springer; 2015. pp. 9–15.
- ↑ Ohuchi H. Wakayama symposium: epithelial-mesenchymal interactions in eyelid development. Ocul Surf. 2012;10:212–6.
- ↑ Tawfik, H., Abdulhafez, M., Fouad, Y., & Dutton, J. (2016). Embryologic and Fetal Development of the Human Eyelid. Ophthalmic Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery, 32(6), 407-414.
- ↑ Tawfik HA, Dutton JJ. Embryologic and Fetal Development of the Human Orbit. Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg. 2018 Sep/Oct;34(5):405-421.
- ↑ Isenberg, S. (1998). Development of Tearing in Preterm and Term Neonates. Archives Of Ophthalmology, 116(6), 773. doi: 10.1001/archopht.116.6.773
- ↑ Jump up to: 6.0 6.1 6.2 Fuhrmann S. Eye morphogenesis and patterning of the optic vesicle. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2010;93:61-84.
- ↑ Creuzet S, Vincent C, Couly G. Neural crest derivatives in ocular and periocular structures. Int J Dev Biol. 2005;49(2-3):161-71.
- ↑ Davis-Silberman N, Ashery-Padan R. Iris development in vertebrates; genetic and molecular considerations. Brain Res. 2008 Feb 04;1192:17-28.
- ↑ Zhao S, Chen Q, Hung FC, Overbeek PA. BMP signaling is required for development of the ciliary body. Development. 2002 Oct;129(19):4435-42.
- ↑ Cvekl A, Tamm ER. Anterior eye development and ocular mesenchyme: new insights from mouse models and human diseases. Bioessays. 2004 Apr;26(4):374-86.
- ↑ Edward DP, Kaufman LM. Anatomy, development, and physiology of the visual system. Pediatr Clin North Am. 2003 Feb;50(1):1-23.
- ↑ Cho, R., & Kahana, A. (2021). Embryology of the Orbit. Journal Of Neurological Surgery Part B: Skull Base, 82(01), 002-006.
- ↑ Tawfik, H., & Dutton, J. (2018). Embryologic and Fetal Development of the Human Orbit. Ophthalmic Plastic & Reconstructive Surgery, 34(5), 405-421.
- ↑ Kruijt Spanjer, E., Bittermann, G., van Hooijdonk, I., Rosenberg, A., & Gawlitta, D. (2017). Taking the endochondral route to craniomaxillofacial bone regeneration: A logical approach?. Journal Of Cranio-Maxillofacial Surgery, 45(7), 1099-1106.
- ↑ Zagozewski JL, Zhang Q, Eisenstat DD. Genetic regulation of vertebrate eye development. Clin Genet. 2014 Nov;86(5):453-60.
- ↑ Torres M, Gómez-Pardo E, Gruss P. Pax2 contributes to inner ear patterning and optic nerve trajectory. Development. 1996 Nov;122(11):3381-91.