Ophthalmic Images in Diverse Patient Populations: Difference between revisions
m (→update images) |
m (→update images) |
||
| Line 418: | Line 418: | ||
<gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | <gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | ||
File:A_Singapore_patient_with_a_macular_hole.jpg|Color photo of macular hole in a patient from Singapore | File:A_Singapore_patient_with_a_macular_hole.jpg|Color photo of macular hole in a patient from Singapore | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Melanoma (conjunctiva) == | == Melanoma (conjunctiva) == | ||
| Line 544: | Line 540: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== Posterior uveitis == | |||
<gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | |||
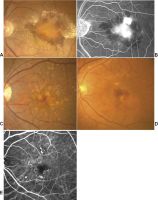
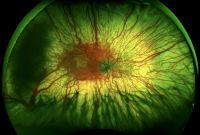
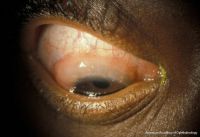
File:posterior_uveitis.jpg|A 69-year-old African American female patient with posterior uveitis shows optic nerve head and choroidal granuloma | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Primary angle closure and OCT == | |||
<gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | |||
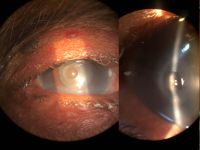
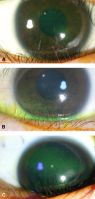
File:Primary_Angle_Closure_Using_OCT_in_Asians.jpg|Anterior segment optical coherence tomography image of nasal and temporal angles showing apposition between the peripheral iris and angle wall anterior to the scleral spur | |||
</gallery> | |||
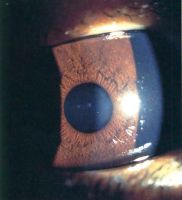
== Primary acquired melanosis (PAM) == | == Primary acquired melanosis (PAM) == | ||
<gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | <gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | ||
| Line 554: | Line 558: | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== | == Ptosis == | ||
<gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | <gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | ||
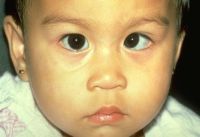
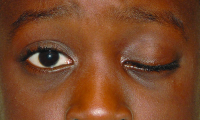
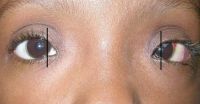
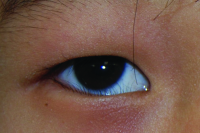
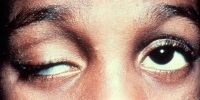
File:Congenital_ptosis.jpg|Congenital ptosis | File:Congenital_ptosis.jpg|Congenital ptosis | ||
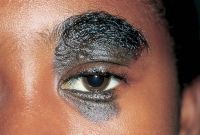
File:Measurement_of_ptosis_in_primary_gaze_with_ruler.jpg|Measurement of ptosis in primary gaze with ruler adjacent to frontal plane of face (MRD1); OD is 4 mm, OS is 1 mm. | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Retinoblastoma == | |||
<gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | |||
File:African-American_patient_with_retinoblastoma.jpg|Case 3. A 3-year-old African-American male patient with a “cloud” in this eye was found to have an iris mass with aqueous seeding (A). By clinical examination and ultrasonography (B), the posterior segment was normal. The iris tumor (A) was sampled by FNAB, demonstrating retinoblastoma. Treatment with chemotherapy and plaque radiotherapy (C) yielded complete resolution of tumor to a calcified scar (D) in the inferotemporal angle. | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Rhinosporidiosis == | |||
<gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | |||
File:AA0_62839.jpg|Fungating irregular granulation tissue in the lower tarsal conjunctiva with multiple pin head whitish lesions over its surface demonstrating underlying mature sporangia. Rhinosporidiosis is a slow-growing chronic inflammatory disorder caused by Rhinosporidiosis seeberi. It is commonly seen in groundwater, infects human beings after coming in contact with contaminated water sources. Commonly seen in nose, ears, and conjunctiva. Easily diagnosed by the typical appearance of whitish pinhead-sized lesions over the surface. Surgical excision is the only modality of management. | |||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
= S-Z = | = S-Z = | ||
== Salzmann’s nodular degeneration == | |||
<gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | |||
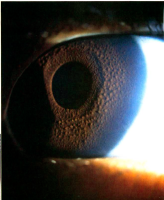
File:Patient_in_India_with_Salzmann’s_nodular_degeneration.jpg|Patient in India with Salzmann’s nodular degeneration | |||
</gallery> | |||
== Scleromalacia perforans == | == Scleromalacia perforans == | ||
<gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | <gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | ||
| Line 577: | Line 595: | ||
File:Indian_patient_with_nixed_staphyloma_anterior.jpg|Mixed staphyloma anterior plus ciliary which is cosmetic blemish on a 4-year-old young boy. | File:Indian_patient_with_nixed_staphyloma_anterior.jpg|Mixed staphyloma anterior plus ciliary which is cosmetic blemish on a 4-year-old young boy. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
== | == Xeroderma pigmentosum == | ||
<gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | <gallery widths="200" heights="200"> | ||
File:Lid_and_ocular_surface_manifestations_in_patients_with_xeroderma_pigment.jpg|Lid and ocular surface manifestations in patients with xeroderma pigmentosum (XP). A, Conjunctival melanosis (arrows) in case 5, an 8-year-old Asian Indian XP-C patient (XP417BE). Note the feeder vessels to lesions (arrows). B, Early pterygium (arrowhead) and lid pigmentation (arrow) in case 2. C, Severe ectropion, entropion, and ocular inflammation in case 3. D, Lid margin keratinization (arrow) and loss of lashes in case 6, a 14-year-old patient (XP243BE). The patient has a history of skin cancer but no history of ocular surface cancer. Lentigines are present on the eyelids, and the patient has bilateral pterygium (arrowhead) and ectropion. The patient has decreased best-corrected visual acuity, possibly due to amblyopia. Localized corneal clouding at the leading edge of pterygium was suspicious for early malignancy, and biopsy was recommended. | File:Lid_and_ocular_surface_manifestations_in_patients_with_xeroderma_pigment.jpg|Lid and ocular surface manifestations in patients with xeroderma pigmentosum (XP). A, Conjunctival melanosis (arrows) in case 5, an 8-year-old Asian Indian XP-C patient (XP417BE). Note the feeder vessels to lesions (arrows). B, Early pterygium (arrowhead) and lid pigmentation (arrow) in case 2. C, Severe ectropion, entropion, and ocular inflammation in case 3. D, Lid margin keratinization (arrow) and loss of lashes in case 6, a 14-year-old patient (XP243BE). The patient has a history of skin cancer but no history of ocular surface cancer. Lentigines are present on the eyelids, and the patient has bilateral pterygium (arrowhead) and ectropion. The patient has decreased best-corrected visual acuity, possibly due to amblyopia. Localized corneal clouding at the leading edge of pterygium was suspicious for early malignancy, and biopsy was recommended. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 15:19, May 11, 2023
All content on Eyewiki is protected by copyright law and the Terms of Service. This content may not be reproduced, copied, or put into any artificial intelligence program, including large language and generative AI models, without permission from the Academy.
Currently, a disproportionate number of textbook figures and photographs are of eye conditions in white patients. Many ocular conditions can appear differently in individuals of color or those with darker skin. The purpose of this page is to share images of both common and rare pathology of the external, anterior, and posterior segments in patients of color. The American Academy of Ophthalmology's Committee for Resident Education’s DEI workgroup initiated this image collection to serve as a source for education and future versions of the Basic and Clinical Science Course (BCSC) and other texts.
Visit the Academy website to learn more about its commitment to diversity, equity, and inclusion in the ophthalmic community and review educational resources related to DEI in ophthalmology.
A-C
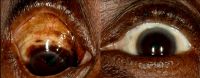
Acanthamoeba keratitis
Amblyopia
Amblyogenic ptosis
Aniridia-associated keratopathy and nystagmus
Arlt's line
Asteroid hyalosis
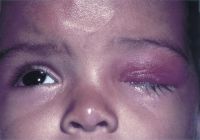
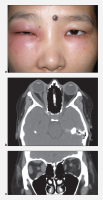
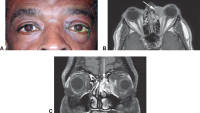
Bacterial orbital cellulitis with proptosis
Bardet-biedl syndrome
Basal cell carcinoma (eyelid)
Bilateral inferior oblique muscle overaction
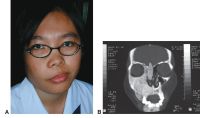
Bilateral scleral thinning
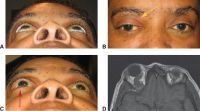
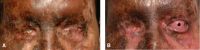
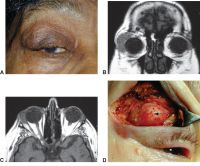
Bilateral nonspecific orbital inflammation (orbital pseudotumor) in an 11-year old Asian boy with a 1-week history of eye pain. Ocular rotation was markedly limited in all directions. CT confirmed proptosis and showed enlargement of all extraocular muscles. Laboratory workup was negative for thyroid disease and rheumatologic disorders. Complete resolution occurred after 1 month of corticosteroid treatment.
Blepharophimosis–ptosis–epicanthus inversus syndrome
Blue nevi
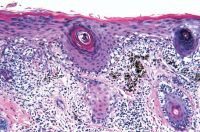
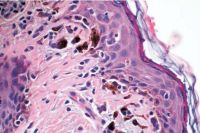
Images from a 71-year-old white Hispanic man. A, Slit-lamp photograph showing moderately pigmented lesions in the forniceal and adjacent palpebral and bulbar conjunctiva (arrow). B, Photomicrograph revealing densely pigmented spindled melanocytes containing copious intracytoplasmic pigment, consistent with blue nevus (arrow; stain, hematoxylin–eosin; original magnification, ×200). C, Photomicrograph demonstrating removal of melanin pigment with bleach and morphologically benign dendritic cells lacking prominent nucleoli (stain, permanganate bleach; original magnification, ×200). D, Photomicrograph demonstrating SOX10 staining (arrows) within the dendritic pigmented melanocytes (stain, SOX10 immunostain with red Chromagen; original magnification, ×400) E, Photomicrograph demonstrating CD68-positive melanophages (arrow) interspersed with the dendritic melanocytes (stain, CD68 immunostain with red Chromagen; original magnification, ×400).
Blue dot cataract
Blunt trauma and ruptured globe
Brown syndrome
Buphthalmos
Carcinoma in situ
Cavernous hemangioma
Cavernous hemangioma. a. Normal exam and appearance. b, c. Axial MRI images demonstrate a well encapsulated, heterogeneously enhancing intraconal tumor in the right orbit. MRI findings of T1 hypointensity, and T2 hyperintensity, are useful in the differential diagnosis from neurofibroma, neurilemmoma, or hemangiopericytomas (these tumors share similar imaging characteristics on CT)
Chalazion
Choroidal metastasis
Cicatricial trachoma
CMV retinitis
Congenital glaucoma, buphthalmos
Congenital coloboma
Congenital lacrimal–cutaneous fistula
Congenital nevocellular nevus
Conjunctival granulomas
Conjunctival papillomas
Conjunctival melanoma
Conjunctival nevus
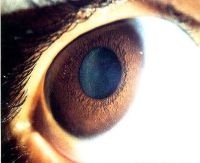
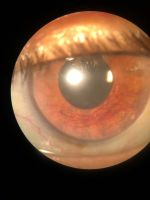
Corneal arcus
Corneal dellen
Corneal ulcer
CRAO (dark choroid)
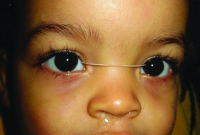
Crawford tube
Crosslinking surgical technique
D-F
Dermoid cyst
Descematocele
Diabetic retinopathy
Figure 1. Color fundus photograph of the left eye in case 1 in 1995 showing lipid exudates (arrow), cotton wool spots, and intraretinal hemorrhages of diabetic retinopathy as well as multiple refractile intraretinal crystals (arrowhead). Figure 2. Color fundus photograph of the left eye in case 1 in 2001 after focal photocoagulation for diabetic macular edema. The edema has completely resolved, and there are fewer intraretinal crystals, which are arranged in a pattern different from that in 1995. Figure 3. Color fundus photograph of the right eye in case 2 showing a frond of retinal neovascularization and many iridescent intraretinal crystals within the foveal avascular zone. Figure 4. Mid-phase fluorescein angiogram of the right eye in case 2 showing the perfused retinal neovascularization and the absence of any fluorescein angiographic sign of the crystals. Figure 5. Color fundus photograph of the right eye in case 2 one year after panretinal laser photocoagulation. Most of the crystals have resolved. Figure 6. Color fundus photograph of the right eye in case 3. The distribution of the intraretinal crystals follows the pattern of the distribution of intraretinal lipid from diabetic macular edema. The diabetic lipid exudates (arrow) can be distinguished from the refractile crystals (arrowhead).
Direct carotid–cavernous fistula (CCF).
Direct carotid–cavernous fistula (CCF). a. Untreated CCF with severe conjunctival chemosis and bilateral oculomotor nerve III palsy. b. Coronal CT images of the orbit demonstrate bilateral dilated superior ophthalmic veins, and enlargement of extraocular muscles. c. Coronal CT images of the cavernous sinus demonstrate convex bowing of the lateral wall. Carotid angiography provides definitive diagnosis. Doppler ultrasound may demonstrate retrograde blood flow in the superior and inferior ophthalmic veins.
Distensible venous malformation
Distensible venous malformation. A, Mild proptosis resulting from venous malformation of the right orbit. B, Fullness of the right superior orbit (arrow). Note the absence of dilated corkscrew conjunctival vessels. C, After Valsalva maneuver, proptosis of the right globe increases (arrow). D, T1-weighted axial MRI shows a venous malformation of the superior ophthalmic vein.
Dystopia canthorum
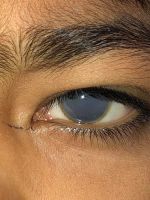
Ectopia lentis
Entrapment
Epiblepharon
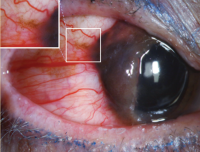
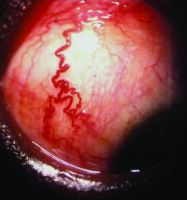
Episcleral vessels
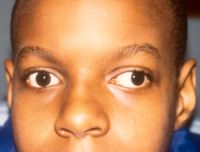
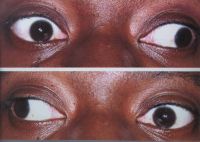
Exotropia
Eyelid laceration involving the canaliculus
Fibrous dysplasia
Fish-eggs phenomenon
Foveal hypoplasia
Fungal ulcer
G-I
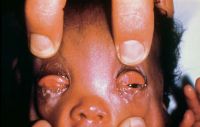
Gonococcal (neisseria) conjunctivitis
Granular corneal dystrophy
Gunderson conjunctival flap
Heerfordt syndrome sarcoid parotitis, lymphadenitis, and uveitis
Herpetic dendrite
Skin vesicles of herpes simplex virus
Hurler's syndrome
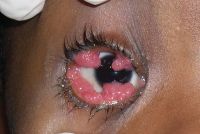
Horner-trantas dots
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
Conjunctival papillomas are associated with human papillomavirus (HPV) infection. In children, the lesions are typically manifestations of an infection acquired during delivery. In adults, conjunctival apillomas are most likely venereal and are often associated with anogenital lesions. Papillomas due to HPV more frequently rogress to malignancy in patients with the human munodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. Human papillomavirus types 6, 11, 16, and 18 have been identified in benign and malignant conjunctival lesions using various antigen and DNA detection techniques.
Intracorneal hemorrhage
Intralenticular metallic foreign body
Patient in IndiaIntralenticular metallic foreign body (IOFB) has been reported in 10% to 41% of open globe injuries. Mechanism of injury is predictive of the presence of IOFBs. High-velocity, relatively small particles are the most common foreign bodies found in the eye. Hammering, grinding, or shaving metal, machine yard work such as lawn mowing, and explosives exposure are particularly high risk.
Iris nodular nevi
Iris melanoma
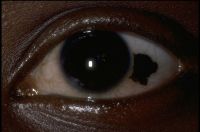
Iris nevus
J-L
Keratoglobus
Kaposi sarcoma lesions
Keratopathy
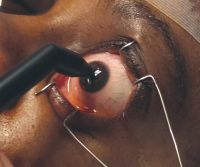
Keratoprosthesis surgery
Laser peripheral iridotomy and anterior chamber angle
Lateral canthotomy/cantholysis
Lattice lines
Lattice corneal dystrophy
Lattice corneal dystrophy (LCD) is an inherited disorder of the eye characterized by the deposition of amyloid resulting in steadily progressive loss of vision. These deposits create linear, “lattice-like” opacities arising primarily in the central cornea, while the peripheral cornea is often spared. They are radially oriented and are accompanied by gradual, superficial opacification of the cornea. Recurrent epithelial erosions are often present, causing ocular irritation and additional vision loss.
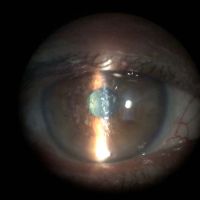
Lens-induced glaucoma
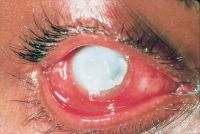
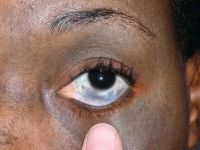
Lens-induced phacolytic glaucoma
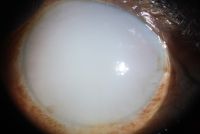
Cloudy cornea in adult – a masquerade of phacolytic glaucoma. A 75 year-old female who in 1 weeks’ time had a total loss of vision, pain, redness, and total whitening of the right eye. Her vision in the right eye was PL + PR inaccurate and the left eye 6/12, N9 with glasses. Intraocular pressure was 60 in the right eye and 14 mm in the left eye. She was diagnosed as having cloudy cornea due to phacolytic glaucoma in the right eye. The patient was managed with I.v. mannitol, topical and systemic steroids, antiglaucoma medications to control IOP and reduce inflammation. After one week she underwent SICS+PCIOL implantation and she regained 6/9, N9 vision after s6 weeks postoperative
Lentigo maligna
Ocular manifestations in leukemias
A, Fundus photograph of a patient with acute lymphoid leukemia, showing multiple Roth spots, superficial and deep hemorrhages, and a subhyaloid bleed involving the macula. B, Fundus photograph of a patient with acute myeloid leukemia, showing dilated tortuous vessels, multiple Roth spots,and a ubhyaloid bleed in the right eye. C, Fundus photograph of a patient with chronic myeloid leukemia with bilateral disc and macular edema, cotton wool spots, Roth spots, retinal infiltrates, and neovascularization of the disc and elsewhere
Limbal vernal keratoconjunctivitis
Lymphoproliferative lesion
A, Right upper eyelid ptosis and fullness with a palpable mass beneath the orbital rim. B, Coronal MRI demonstrating right lacrimal gland enlargement with infiltration of anterior orbital tissues. C, Axial MRI showing characteristic molding of the lesion to adjacent structures. D, Incisional biopsy of the abnormal infiltration of the lacrimal gland reveals orbital lymphoma (arrow).
M-O
Macular dystrophy of the retina, locus 1
Macular hole
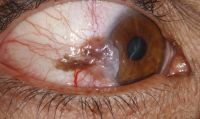
Melanoma (conjunctiva)
Metastatic carcinoma
A 37-year-old presented with ocular metastasis with primary ductal carcinoma of the left breast. The case presented with complaints of redness and pain OS for 1 month, and there was a past history of a left modified radical mastectomy 3 years previously at the same institution where the patient didn’t complete the chemotherapy. On examination, OD-within normal limits, OS lids appeared edematous, circumcorneal congestion with prominent episcleral vessels seen, anterior chamber had exudative deposits and 1+ grade of cellular activity present, iris was atrophied from 3’o-5’o clock hours.
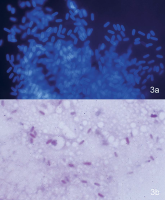
Microsporidial keratoconjunctivitis
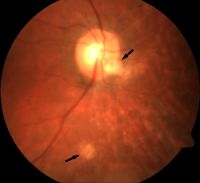
Morning glory disc with exudative RD
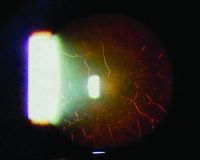
Morning glory syndrome with serous retinal detachment. Enlarged and funnel-shaped excavation of right optic disc with hyperplastic glial tissues in the central disc, peripapillary pigment abnormality, multiple anomalous straight vessels radiating circumferentially from the optic disc, inferior serous retinal detachment from 3 to 9 o'clock.
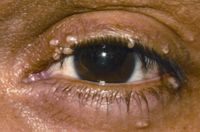
Molluscum contagiosum
Giant eyelid molluscum contagiosum in a child with AIDS. A 6-year-old boy presented with a 3-month history of multiple, pedunculated, nodules with a central umbilication (Fig 1A). A clinical diagnosis of molluscum contagiosum was made and investigations revealed HIV infection with a CD4 count of 124/ml3. Highly active antiretroviral therapy (HAART) was initiated. The larger lesions were excised (Fig 1B). Characteristic eosinophilic intracytoplasmic inclusion bodies were seen on histopathologic examination (Fig 1C; hematoxylin-eosin 40). The child is currently on maintenance therapy with HAART with no recurrence of the lesions.
Mucopolysaccharidosis
Munson sign
Myasthenia gravis
Neovascular glaucoma
Neurofibromatosis type I
Nevus of ota (eyelids)
Oculodermal melanocytosis
Ocular surface squamous neoplasia
Ophthalmia neonatorum
Ophthalmic exam
Optic disk tilting
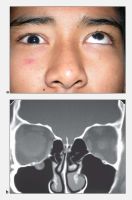
Orbital floor fracture
Orbital floor fracture. A, Teenaged patient following blunt trauma to the eye and orbit. Attempted gaze up and left. The left eye is unable to elevate to midline. (Note: The pupillary dilation is pharmacologic). B, Coronal CT scan of the orbit showing a small orbital floor fracture and inferior rectus muscle prolapsing into the maxillary sinus (arrow). C, Intraoperative view of a similar case showing an orbital floor defect (arrow) enlarged surgically to release and extract inferior rectus muscle. D, Two months postoperatively, the patient demonstrates resolution of upgaze limitation.
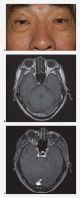
Orbital lymphoma
Orbital lymphoma. a, b. Subacute onset right proptosis and upper lid mechanical ptosis with an absence of inflammatory signs. c. Coronal CT image demonstrates right lateral orbit superior and inferior infiltration by dense homogenous mass that uniformly enhances with contrast administration. Of note, the mass conforms to surrounding structures and extends along fascial planes with little surrounding inflammation. Significant disparity between tumor bulk and lack of proptosis is noted.
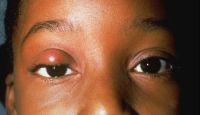
Orbital myositis
Overaction of left inferior oblique
P-R
Papillary conjunctivitis
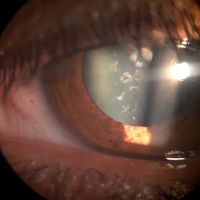
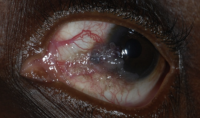
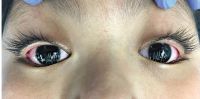
Peripheral ulcerative keratitis
Peripheral ulcerative keratitis is a rare but potentially devastating corneal emergency. It is characterized by crescentic-shaped peripheral ulceration and may involve the sclera and conjunctiva. The etiology includes immune-mediated systemic diseases such as granulomatosis polyangiitis and rheumatoid arthritis, immune-medicated ocular diseases such as Mooren’s ulcer and non-immune mediated conditions, especially infective etiology. A host of other conditions can also mimic this entity. The patient can present in the advanced stage with corneal perforation, necessitating emergency tectonic procedures.
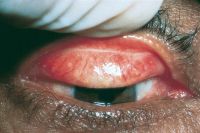
Phlyctenular conjunctivitis
Polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy (PCV)
Posterior segment examination
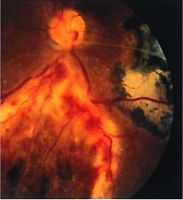
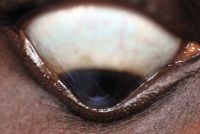
Posterior uveitis
Primary angle closure and OCT
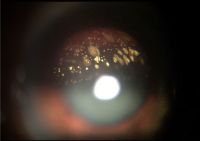
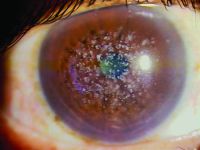
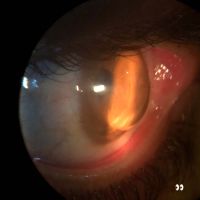
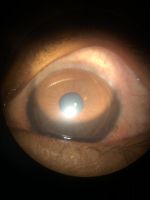
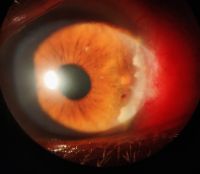
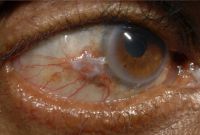
Primary acquired melanosis (PAM)
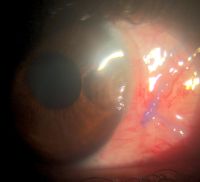
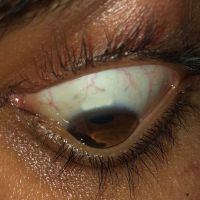
Pterygium
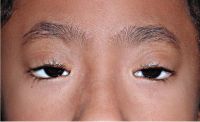
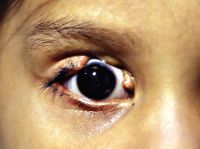
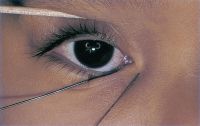
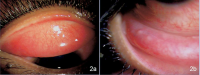
Ptosis
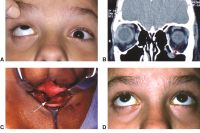
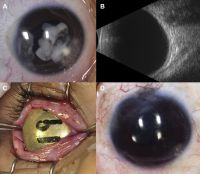
Retinoblastoma
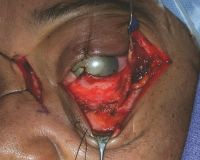
Case 3. A 3-year-old African-American male patient with a “cloud” in this eye was found to have an iris mass with aqueous seeding (A). By clinical examination and ultrasonography (B), the posterior segment was normal. The iris tumor (A) was sampled by FNAB, demonstrating retinoblastoma. Treatment with chemotherapy and plaque radiotherapy (C) yielded complete resolution of tumor to a calcified scar (D) in the inferotemporal angle.
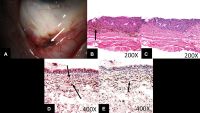
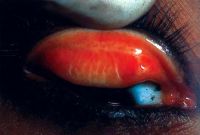
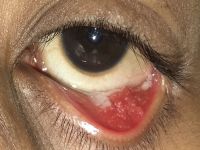
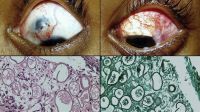
Rhinosporidiosis
Fungating irregular granulation tissue in the lower tarsal conjunctiva with multiple pin head whitish lesions over its surface demonstrating underlying mature sporangia. Rhinosporidiosis is a slow-growing chronic inflammatory disorder caused by Rhinosporidiosis seeberi. It is commonly seen in groundwater, infects human beings after coming in contact with contaminated water sources. Commonly seen in nose, ears, and conjunctiva. Easily diagnosed by the typical appearance of whitish pinhead-sized lesions over the surface. Surgical excision is the only modality of management.
S-Z
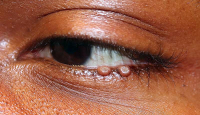
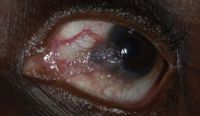
Salzmann’s nodular degeneration
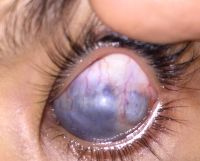
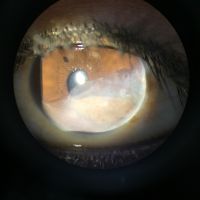
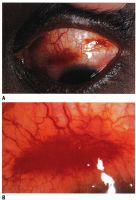
Scleromalacia perforans
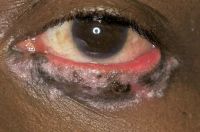
Scleromalacia Perforans from Long-Standing Bulbar Conjunctival Rhinosporidiosis. A 12-year-old child presented with a 6-month old painless, reddish-blue swelling superior to the upper limbus (Fig 1A). Scleral thinning with uveal show and a conjunctival mass with dot-like, yellowish-white surface excrescences were noted. Excision with a donor scleral patch graft was performed (Fig 1B). Histopathology showed partially separated squamous metaplastic epithelium(Fig 1CeD,), edematous stroma, and numerous thick walled sporangia indicating rhinosporidiosis. Several of these appeared degenerated and empty. Others showed granular debris material (Fig 1C, Hematoxylin-Eosin; Fig 1D, Gomori’s MethenamineSilver 400). Ocular rhinosporidiosis most commonly involves the tarsal conjunctiva. Scleral melt from bulbar conjunctival rhinosporidiosis is known but extremely rare.
Squamous cell carcinoma
Staphyloma anterior
Xeroderma pigmentosum
Lid and ocular surface manifestations in patients with xeroderma pigmentosum (XP). A, Conjunctival melanosis (arrows) in case 5, an 8-year-old Asian Indian XP-C patient (XP417BE). Note the feeder vessels to lesions (arrows). B, Early pterygium (arrowhead) and lid pigmentation (arrow) in case 2. C, Severe ectropion, entropion, and ocular inflammation in case 3. D, Lid margin keratinization (arrow) and loss of lashes in case 6, a 14-year-old patient (XP243BE). The patient has a history of skin cancer but no history of ocular surface cancer. Lentigines are present on the eyelids, and the patient has bilateral pterygium (arrowhead) and ectropion. The patient has decreased best-corrected visual acuity, possibly due to amblyopia. Localized corneal clouding at the leading edge of pterygium was suspicious for early malignancy, and biopsy was recommended.